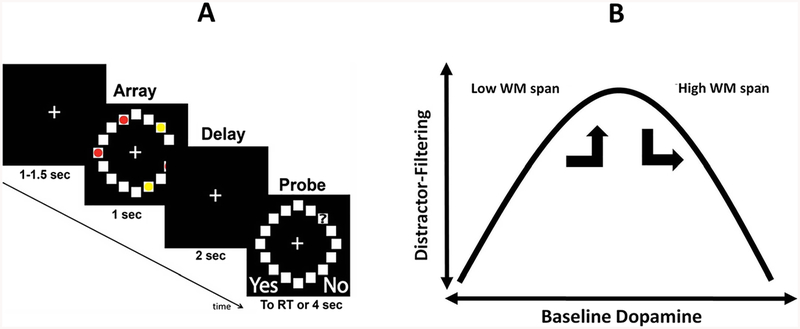
Fig. 1.
a Trial events and temporal parameters of the visuospatial working memory (VSWM) task. Participants responded whether the square currently occupied by the probe (?) had been occupied by a red dot (in the preceding visual array). Participants were instructed to ignore yellow dots. Visual arrays showed either 3 targets (Condition 3), 3 targets plus two distractors (Condition 3+2; depicted in Fig.), or 5 targets (Condition 5). See main text for additional details. b Hypothetical inverted-U function relating baseline DA to distractor-filtering ability. It was predicted that cabergoline would push individuals with higher working memory (WM) span out of an optimal position on the curve, resulting in a greater VSWM capacity decrement for these individuals due to the presence of distractors, compared to placebo. In contrast, cabergoline would push individuals with lower WM span into the optimal position, resulting in a smaller VSWM capacity decrement for these individuals due to the presence of distractors, compared to placebo