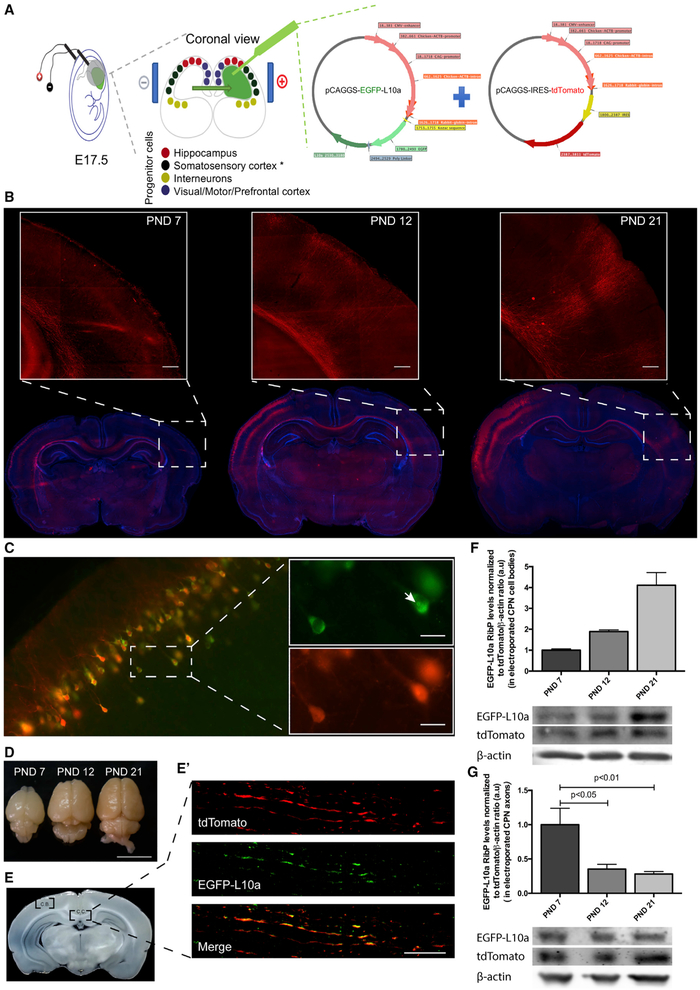
Figure 1. Axonal Ribosome Reduction Correlates with Synaptogenesis In Vivo.
(A) In utero electroporation experimental design for rat embryonic somatosensory cortex progenitor cells.
(B) Development of CPN in vivo at different post-natal days (PND). tdTomato (red) was used as a reporter protein to allow corpus callosum visualization and DAPI (blue) as nuclear marker. Inset scale bar is 250 μm.
(C) EGFP-tagged ribosomal protein (RibP) L10a and tdTomato are co-expressed at somatosensory cortex. Co-expression of tdTomato (red) and RibP L10a (green) at somatosensory cortex cell bodies (C) is shown. Nucleolus position is indicated by the white arrow in the top inset (C). Scale bar is 25 μm.
(D–G) RibP L10a levels are reduced in CPN axons as they reach the contralateral target area but do not decrease in callosal CPN cell bodies. Electroporated brains, at different PND after perfusion and fixation (D; Scale bar is 1 cm), are shown. Corpus callosum (C.C.) midline area and cell bodies (C.B.) regions were used for protein extraction (E). Representative image of CPN cell bodies region (C; tdTomato; red) or corpus callosum midline area containing CPN axons (tdTomato; red) and RibP L10a (green) (E′; scale bar is 15 μm) is shown. Western blot analysis of EGFP and tdTomato expression (F and G) is shown. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 2 (F) or 4 (G) independent experiments. For each independent experiment, results were normalized to tdTomato/β-actin ratio. Statistical significance by one-way ANOVA followed by multiple-comparison Tukey’s post hoc test is shown.