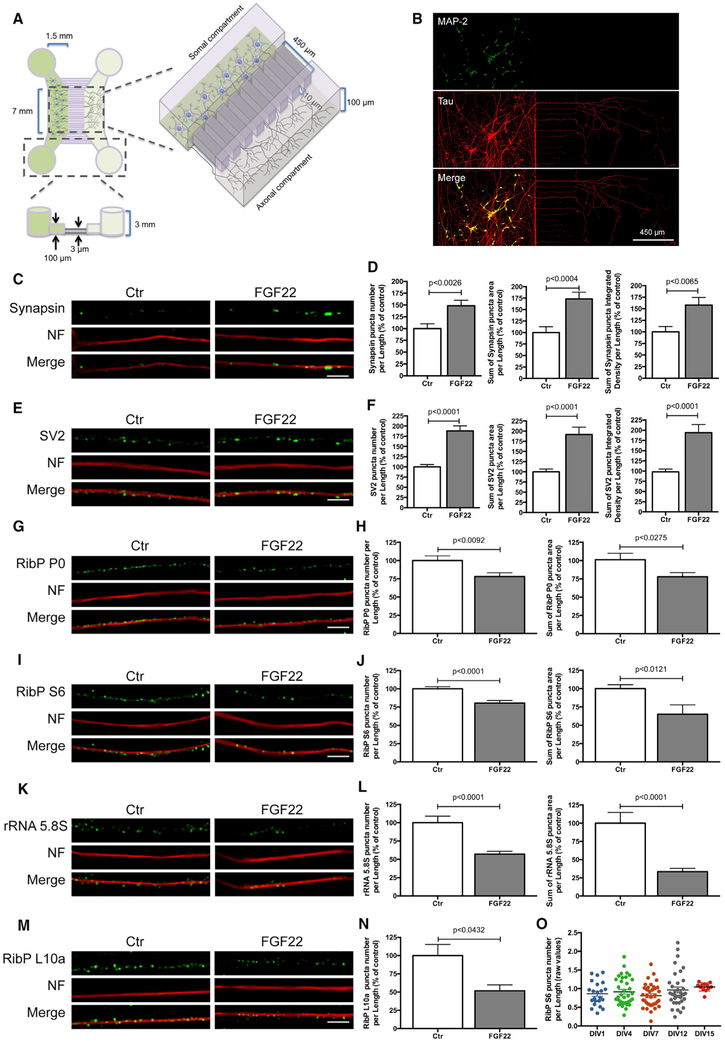
Figure 2. Axonal Application of FGF22 Induces Synapse Formation and RibPs and rRNA 5.8S Decrease.
(A) Schematic representation of microfluidic chambers.
(B) Representative image of spinal motor neurons (MNs) cultured in microfluidic chambers. At DIV 4, neurons were immunostained against MAP2 (somatodendritic marker; green) and Tau (axonal marker; red).
(C and E) Presynaptic clusters increase upon FGF22 treatment. At DIV 3/4, MN axons were stimulated with either BSA (Ctr) or FGF22 (2 nM). At DIV 4, neurons were immunostained against synapsin (C) or SV2 (E) (green) and neurofilament (NF; red). Scale bar is 2.5 μm.
(G, I, and K) Rib P and rRNA 5.8S decrease upon FGF22 treatment. At DIV 3/4, MN axons were stimulated with either BSA (Ctr) or FGF22 (2 nM). At DIV 4, neurons were immunostained against RibP P0 (G), RibP S6 (I), or rRNA 5.8S (K; green) and neurofilament (NF; red). Scale bar is 2.5 μm.
(D, F, H, J, and L) Quantitative data of the number, area, and integrated density of synapsin (D) and SV2 (F) and number and area of RibP P0 (H) RibP S6 (J) and rRNA 5.8S (L) clusters per axonal length. Bars represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance by unpaired Student’s t test.
(M) Exogenous RibP EGFP-L10a decrease upon FGF22 treatment. MNs were transduced at DIV 1 with an EGFP-RibP L10a lentivirus and stimulated at DIV 3/4, with either BSA (Ctr) or FGF22 (2 nM). Neurons were immunostained against GFP (green) and neurofilament (NF; red). Scale bar is 2.5 μm.
(N) Quantitative data of the number of RibP L10a clusters per axonal length. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 2 independent experiments. Statistical significance by unpaired Student’s t test.
(O) Ribosomal levels are constant in developing axons. Unstimulated MNs were maintained in culture for increasing time periods (DIV 1–15). At the indicated points, neurons were fixed and immunostained against RibP S6 and neurofilament. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 1–3 independent experiments. No significant differences were found among the groups, using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc statistic test.