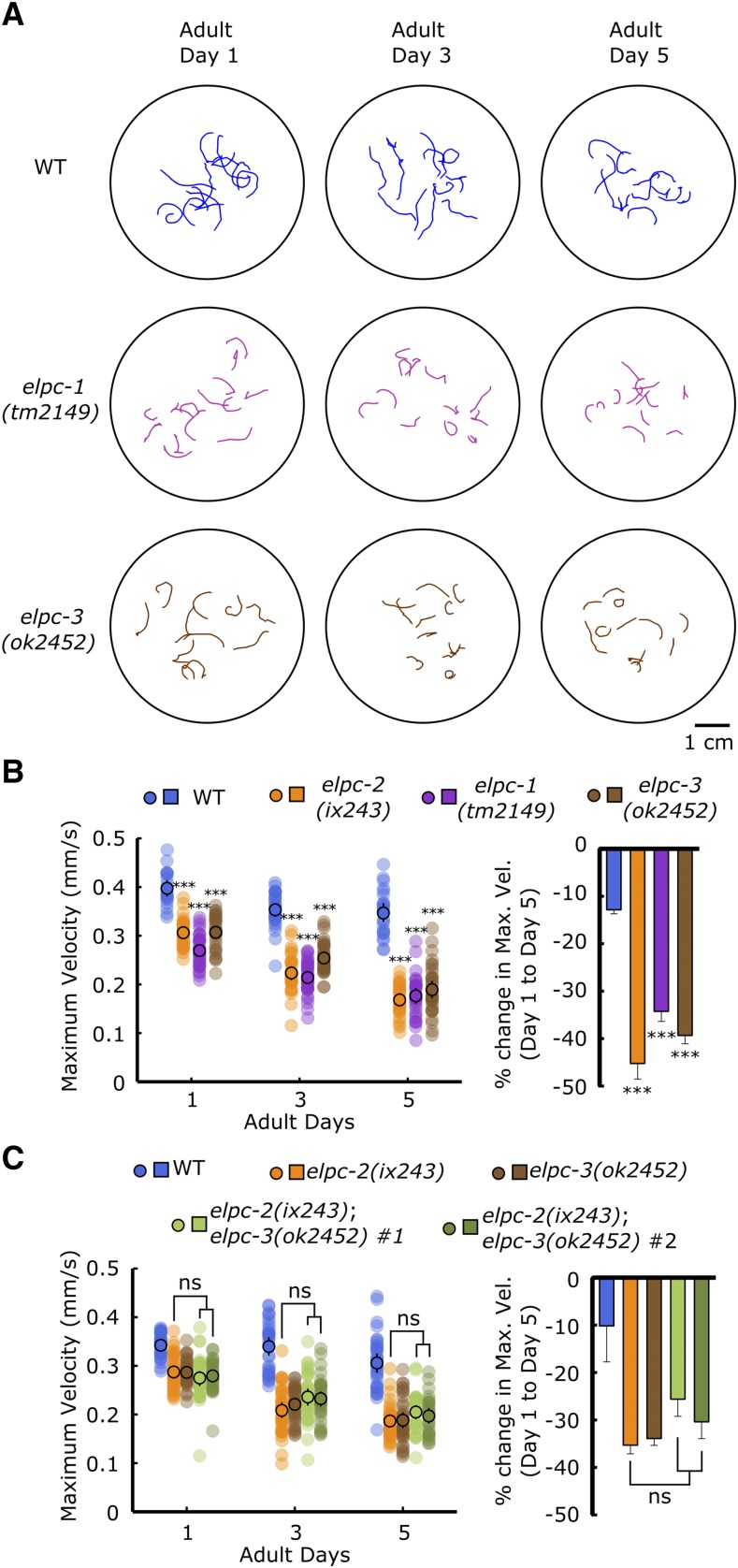
Figure 5.
The Elongator complex is required to maintain locomotor ability (A) Representative locomotor tracks of WT, elpc-1(tm2149) and elpc-3(ok2452) worms. n = 10–15 tracks per plate. (B) (Left) Maximum velocities of WT, elpc-1(tm2149), and elpc-3(ok2452) worms. (Right) Percent change in maximum velocity of worms from left panel. (C) (Left) Maximum velocities of WT, elpc-2(ix243), elpc-3(ok2452), and elpc-2(ix243);elpc-3(ok2452) worms. (Right) Percent change in maximum velocity of worms from left panel. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. For maximum velocity experiments, n = 30–45 worms per strain for each day (10–15 worms from 3 biological replicate plates). For percent change in maximum velocity graphs, n = 3 biological replicate plates. ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant; One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test vs. WT for B; One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for C.