Figure 1.
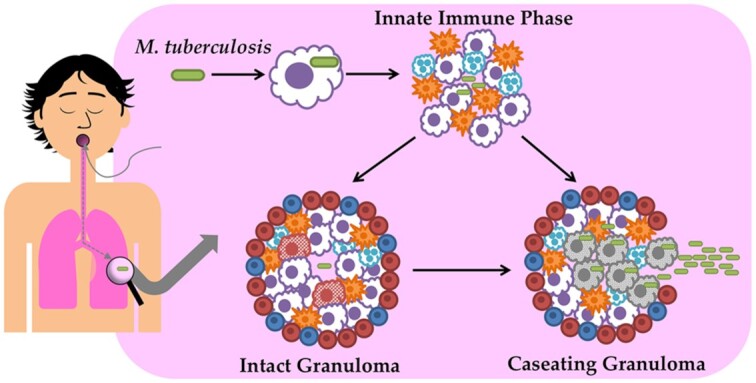
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is spread via aerosols and is harbored primarily in the lungs. When macrophages encounter and engulf the pathogens, it may be eliminated or may persist due to compensatory mechanisms. During the innate immune phase, macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells are recruited to the site of infection. After severeal week, T and B cells migrate to the site of infection and form granulomas that encapsulate the innate immune cells and bacilli in a fibrotic capsule that creates a gradient of hypoxia. If the immune cells are not able to kill the bacilli and prevent its growth, granulomas caseate and Mtbbacilli disseminate to other organs including the spleen, liver and brain.
