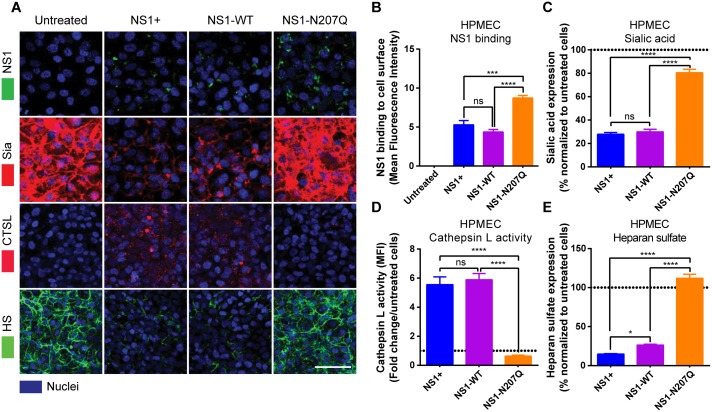
Fig 2. Mutation of the N-glycosylation site 207 prevents DENV NS1-induced cathepsin L and sialidase activation and EGL disruption on endothelial cells.
(A) NS1 protein binding (green, top row) to HPMEC 6 hpt at 37°C was visualized via IFA. The integrity of the EGL was assessed by the presence of sialic acid (Sia) surface expression, stained with WGA-A647 (red, 2nd row; merge of NS1 and Sia), as well as cathepsin L (CTSL) activity (red, 3rd row) and heparan sulfate [9] surface expression (green, bottom row), in HPMEC 6 hpt with NS1 at 37°C, as visualized via IFA. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Images (20X; scale bars, 50 μm) are representative of 2 independent experiments. (B) Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) was used to quantify the amount of NS1 binding to the cell surface, (C) sialic acid surface expression, (D) cathepsin L activity, and (E) heparan sulfate expression on HPMEC in Fig 2A. The means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of two individual experiments run in duplicate are shown. ns = not significant; *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001.