Figure 5.
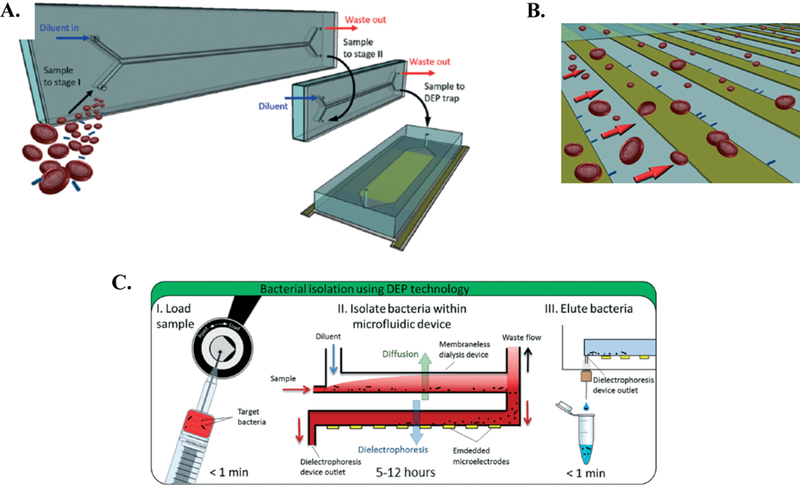
Dielectrophoretic platform for isolation of bacteria from blood proposed by D’Amico et al 21. A. Schematic of the integrated microfluidic dialysis-dielectrophoresis isolation system. Two MMDs are connected in series, followed by the active dielectrophoresis device. B. Sample flow through separation microchip. Bacteria (green) are attracted to electrodes, while other blood components are repelled and washed through the device. C. Overview of proposed workflow. Following separation, sample is eluted from device for molecular analysis. Republished with permission of Royal Society of Chemistry from, Isolation and concentration of bacteria from blood using microfluidic membraneless dialysis and dielectrophoresis, D’Amico et al., 17, 2017; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
