Figure 9.
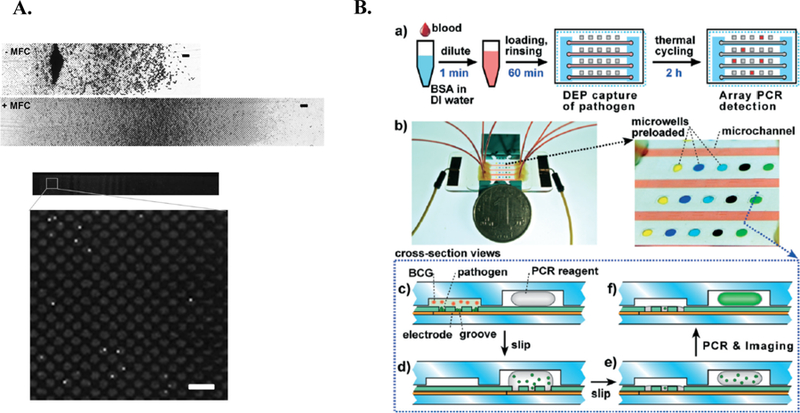
Integrated on-chip isolation and detection platform. A. Overview of Cooper et al. Image of microchannel without (top) and with (middle) magnetic field concentrator (MFC). First half of channel is shown (scale bar = 50μm). Fluorescent image displaying captured C. albicans following immunofluorescent staining (bottom) 20. Further, the magnetic field concentrator (MFC) minimizes magnetic bead clumping (middle), allowing for optical detection (bottom)20. Republished with permission of Royal Society of Chemistry from, A microdevice for rapid optical detection of magnetically captured rare blood pathogens, Cooper et al., 14, 2014; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc. B. Overview of Cai et al. integrated methodology. a) Schematic of workflow. b) relative size of microdevice (left) with zoomed in image of microchannel and preloaded microwells. c-f) cross-sectional view of device operation. Pathogen is retained in grooves, while blood cells (BCG) are washed away. Device is “slipped” to expose liquid PCR reagents to pathogen. Device is returned to original position avoid contaminated surface. Device is thermocycled in situ and imaged 15. Republished with permission of Royal Society of Chemistry from, An integrated microfluidic device utilizing dielectrophoresis and multiplex array PCR for point-of-care detection of pathogens, Cai et al., 14, 2014; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
