Figure 1.
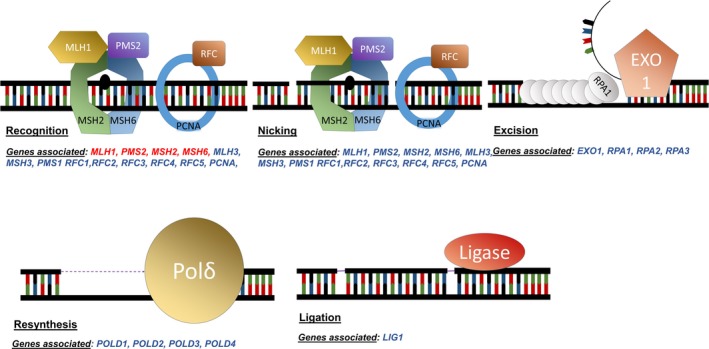
Mismatch repair pathway major steps with genes associated. Genes in red are the one usually screened for mutations in a clinical setting. MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, and MSH6 are all involved in the recognition of DNA damage. PMS2 has an endonuclease function in nicking around the damaged region. EXO1 will then remove the DNA strand containing the error and RPA (Replication Protein A) will protect the remaining single strand of DNA. The DNA polymerase Polδ resynthesises the new DNA strand which is then ligated with a ligase (based on Hsieh & Yamane, 2008)
