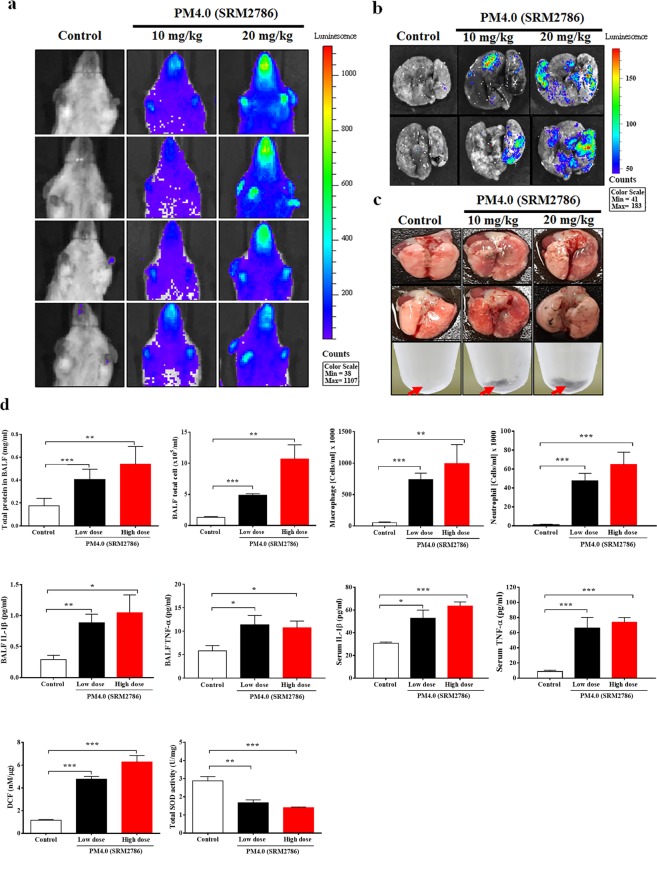
Figure 1.
Effects of PM4.0 exposure on inflammation in NF-κB-luciferase+/+ transgenic mice. (a,b) Bioluminescence imaging of the chest cavity and lung tissue of transgenic NF-κB+/+ mice after exposure to saline solution, 10 and 20 mg/Kg of PM4.0 for 4 weeks. (c) Both PM4.0-exposed transgenic mice had more black particle deposition in the BALF and lung tissue than the control group. Red arrow: PM4.0 aggregation. (d) PM4.0 exposure increased the total cell and total protein levels, the macrophage and neutrophil cell counts, the inflammatory cytokine (IL-1β, TNF-α) levels, and the DCF (ROS) levels in BALF; decreased of total SOD activity in lung tissue; increased the circulating inflammatory cytokine (IL-1β, TNF-α) levels in serum compared to those in the control group. n = 8 per group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the control group.