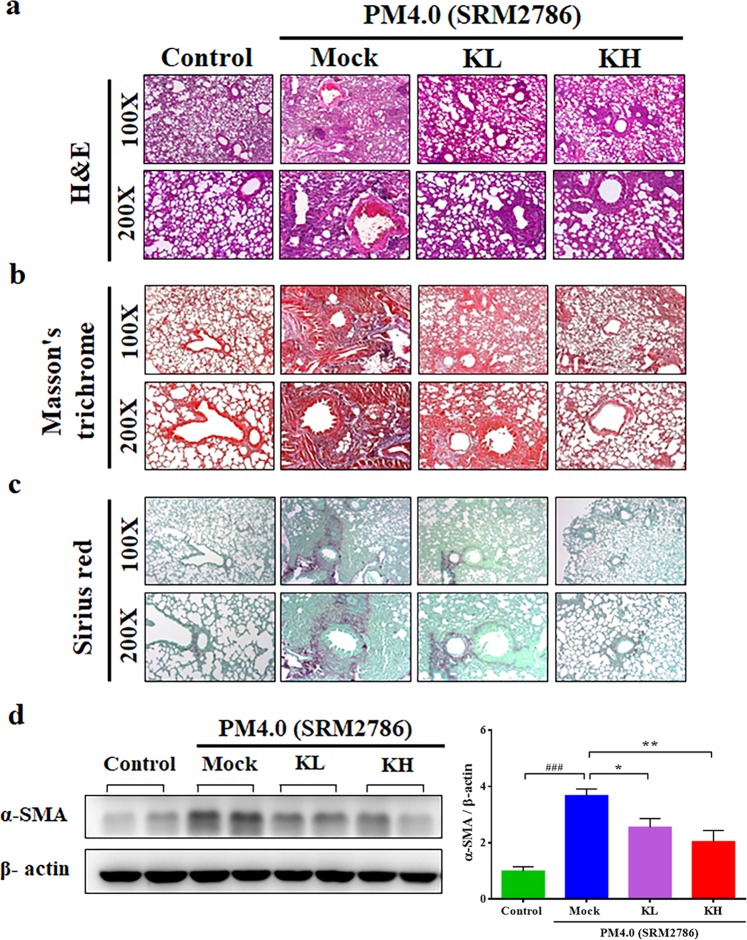
Figure 6.
Kefir peptides improved the PM4.0-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in NF-κB-luciferase+/+ transgenic mice. (a) Morphologic features of the mice lung inflammation observed by H&E staining. Kefir peptides reduced the PM4.0-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice compared with that in the PM4.0/Mock group. (b) The collagen deposition in the lung tissue of the mice was observed by Masson’s trichrome staining. Kefir peptides reduced the PM4.0-induced collagen deposition in the pulmonary tissue of the mice compared that in the PM4.0/Mock group. (c) Collagen fibers in the lung tissue of the mice were observed by Sirius red staining. Kefir peptides reduced the PM4.0-induced collagen fibers in the pulmonary tissue of mice compared with that in the PM4.0/Mock group. The scale bars in all images indicate 100 μm. Lower magnification (100x) images of lung tissues are shown in the upper panel. Higher magnification (200x) images are shown in the lower panel. (d) Changes in the protein expression level of α-SMA in different groups normalized to an internal control, β-actin. Kefir peptides reduced the PM4.0-induced protein expression levels of α-SMA compared that in the PM4.0/Mock group; the levels were normalized to the internal control, β-actin. Representative images of the protein expression levels assayed by Western blotting. n = 8 per group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. ###p < 0.001 compared to the control group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the PM4.0/Mock group.