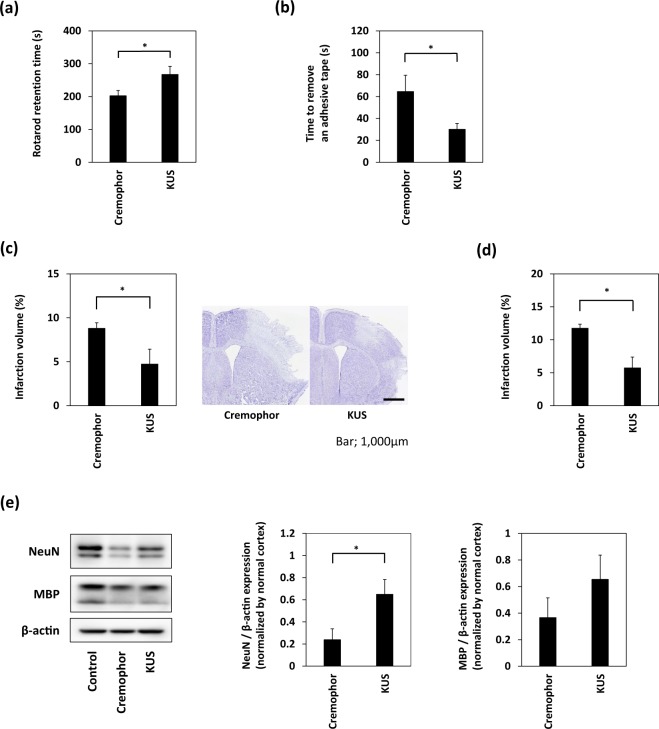
Figure 3.
Treatment with KUS121 improves functional deficits and reduces brain infarction volume. (a) Rotarod retention time and (b) the time to remove an adhesive tape in C57BL/6 mice subjected to transient occlusion of the distal portion of left middle cerebral artery (MCA). Neurological function was measured by the accelerating rotarod apparatus and adhesive removal test 24 h after occlusion of the distal MCA (n = 16; *p < 0.05). (c) Quantification of the infarction volume was calculated by Nissl staining and representative Nissl stained brain sections of C57BL/6 mice (Scale bar: 1,000 μm; vehicle, n = 5; KUS121, n = 4; *p < 0.05). (d) Quantification of the infarction volume in B-17 mice measured 24 h after transient occlusion of the distal MCA and calculated by Nissl staining (vehicle, n = 4; KUS121, n = 5; *p < 0.05). (e) Western blot analyses of cerebral cortex lysates for Neuronal Nuclei (NeuN) and myelin basic protein (MBP). The cerebral cortex of B-17 mice was collected 24 h after transient occlusion of the distal MCA. The ratio of NeuN or MBP to β-actin expression levels was calculated (n = 5; *p < 0.05).