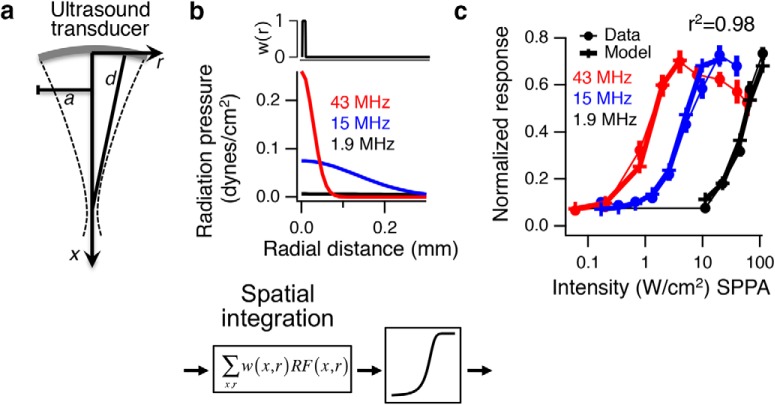
Figure 7.
A radiation force model predicts responses in the retina. a, An analytic expression was used to calculate radiation force in a cylindrical coordinate system based on transducer characteristics. a, Radius of transducer; d, focal distance; f, frequency; I, intensity; x, axial distance; r, radial distance, from Rudenko et al. (1996). b, Radiation force model of retinal response. Cumulative radiation pressure at I = 1 W/cm2 is shown versus radial distance for the three frequencies. The radiation force is multiplied by a spatial weighting function, which in the retina is very small (∼10 μm) and equivalent to the peak radiation force, and then passed through an optimized sigmoidal nonlinearity to generate the model responses. c, Normalized population response for 43, 15, and 1.9 MHz as a function of intensity is compared with the radiation force model output (n > 20 cells in each case).