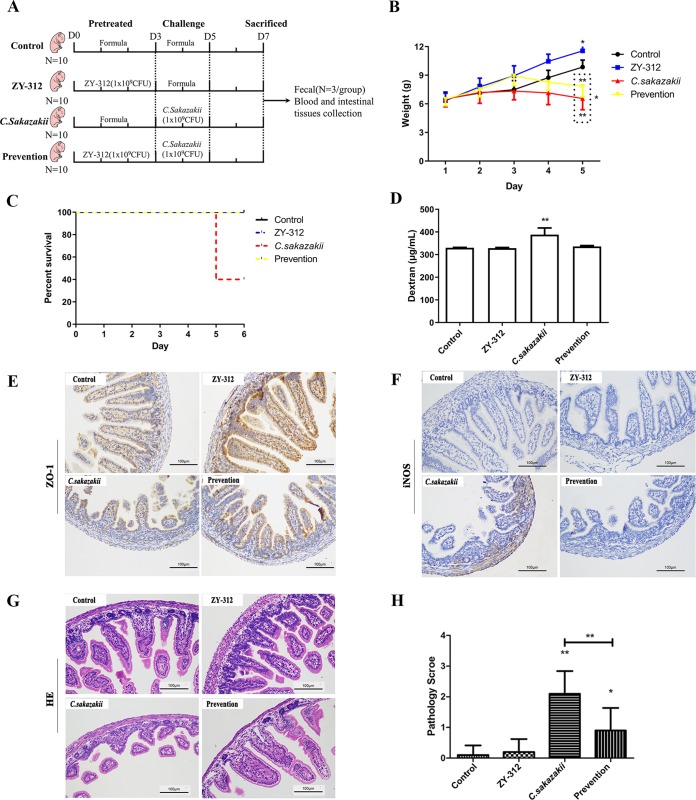
FIG 2.
ZY-312 ameliorates C. sakazakii-induced effects on the intestinal integrity and attenuates clinical symptoms and intestinal inflammation during the pathological process of C. sakazakii-induced NEC in neonatal rats. (A) Experimental design for four groups. Rats were fed with 0.2 ml of a formula containing 1 × 109 CFU of ZY-312 or formula alone once per day from day 0 to day 3. Then, the rats were fed with a 0.2 ml C. sakazakii formula (1 × 109 CFU) once per day and exposed thrice to a hypoxia exposure regime (5% O2 and 95% N2) or to formula alone from day 3 to day 5. On day 7, rats were sacrificed and feces samples (n = 3 in each group), blood, and intestinal tissues were collected for the next experiments. (B) Body weight changes of neonatal rats during C. sakazakii infection. (C) Mortality rate evaluation in neonatal rats during C. sakazakii infection. (D) The intestinal barrier permeability was determined by quantifying serum concentrations of FITC-dextran. (E) Immunohistochemical staining showing the expression levels of the tight junction protein ZO-1 in the intestines of neonatal rats. (F) Immunostaining of iNOS in the intestinal tissue of neonatal rats. (G) Representative images of intestinal tissue (stained with H&E) from neonatal rats subjected to various treatments. (H) Semiquantitative pathology scores of intestinal tissues from neonatal rats subjected to various treatments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.