Figure 2.
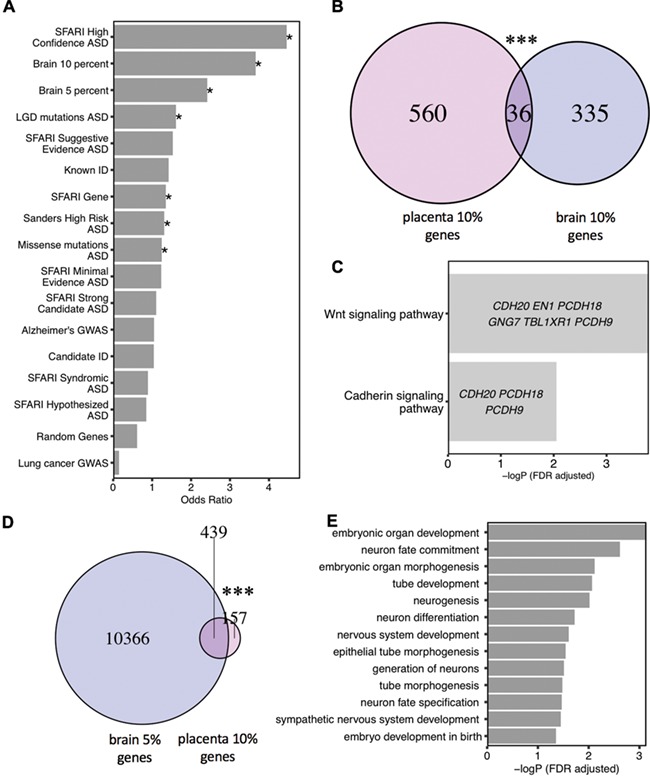
Placenta ASD DMR genes overlapped with ASD DMR associated genes from postmortem brain and known genetic risk for ASD but not for other disorders. (A) Placenta ASD DMR associated genes were compared for significant overlap with ASD DMR genes identified from ASD postmortem brain (33) (based on 10% or 5% methylation difference cutoffs), as well as multiple curated gene lists of ASD, ID or unrelated disorder genetic risks or a randomly generated gene list (*P < 0.05 FDR corrected two-tailed Fisher’s exact test, ranked by odds ratio). SFARI: Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative (34), LGD: likely gene-disrupting mutation, ASD: autism spectrum disorder, Alzheimer: Alzheimer’s Disease, ID: intellectual disability. (B) Venn diagram represents the significant overlap of 36 genes associated with placenta ASD DMRs and brain ASD DMRs based on 10% methylation differences in brain between ASD versus TD by Fisher’s exact test (P < 0.001***) (Supplementary Material, Table 7). Methylation data from human postmortem brain was obtained from previous published data sets, GSE8154 (ASD and TD) (33). (C) GO and pathway analysis on the 36 genes in common between placenta ASD DMRs and brain ASD DMRs associated genes. Enrichment tests were done on Fisher’s exact test with FDR 0.05 correction. Genes in each GO term are shown within each bar. (D) Venn diagram represents significant overlap of 439 genes between placenta ASD DMRs and DMRs from brain with 5% methylation difference between ASD and TD (Fisher’s exact test, P < 0.001***) (Supplementary Material, Table 7). (E) Multiple developmental pathways were significantly enriched on the overlapped 439 genes with Fisher’s exact test after FDR 0.05 correction.
