Figure 3.
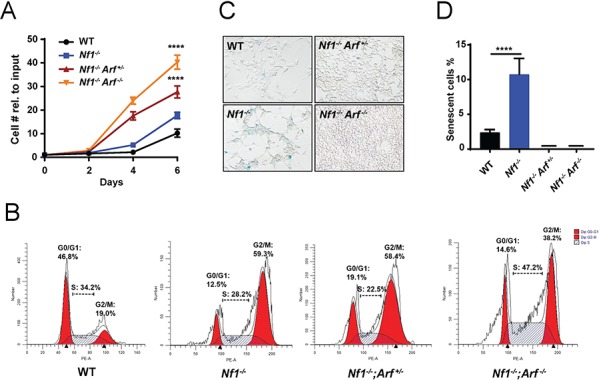
Genetic ablation of p19Arf allows Nf1-null DNSCs to escape senescence and proliferate aberrantly. (A) Proliferation of WT, Nf1−/−, Nf1−/−;Arf +/− and Nf1−/−;Arf −/− DNSCS was assessed by manual cell counting at serial time points as shown. The fold change in cell number relative to input (50 000 cells/well) is shown. (B) Cell cycle of WT, Nf1−/−, Nf1−/−;Arf +/− and Nf1−/−;Arf −/− DNSCS was assessed by flow cytometry. The percentage of cells in G0/G1, S and G2/M phase are denoted as shown. (C) Senescence associated β-galactosidase staining in DNSCs as shown in representative photomicrographs. (D) The percentage of SAS-βgal-positive staining cells relative to total cell number per HPF was quantified. ****P < 0.0001 for Nf1−/− versus WT, Nf1−/−;Arf +/− and Nf1−/−;Arf −/− by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison’s test. n = 3 biological replicates per genotype.
