Figure 4.
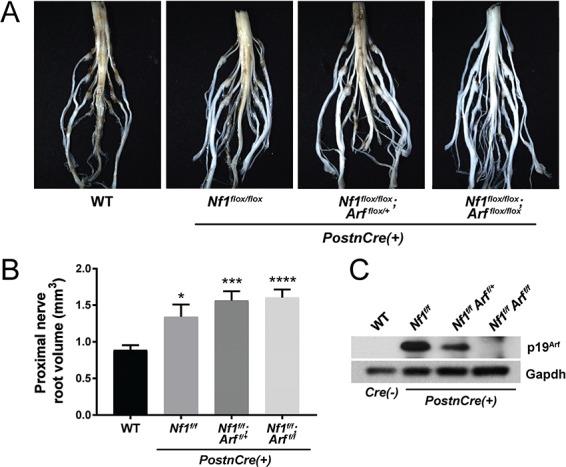
Diffuse morphological changes in the lumbosacral nerve plexus of Nf1/Arf mutant mice. (A) The lumbosacral spinal cord, DRG and associated proximal spinal nerve roots were microdissected from each genotype: WT, Nf1flox/flox, Nf1flox/flox;Arf flox/+ and Nf1flox/flox;Arf flox/flox;PostnCre(+) as shown. (B) Proximal spinal nerve root volume was measured. The number of proximal spinal nerve roots evaluated per genotype are as follows: WT (n = 28), Nf1flox/flox;PostnCre(+) (n = 16), Nf1flox/flox;Arf flox/+;PostnCre(+) (n = 16) and Nf1flox/flox;Arf flox/flox;PostnCre(+) (n = 24). *P < 0.05 WT versus Nf1flox/flox;PostnCre(+).***P < 0.001 WT versus Nf1flox/flox;Arf flox/+;PostnCre(+).****P < 0.0001 WT versus Nf1flox/flox;Arf flox/flox;PostnCre(+). Statistical analysis was performed via one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison test. (C) Western blot of p19Arf and Gapdh (loading control) in the trigeminal nerve of each genotype.
