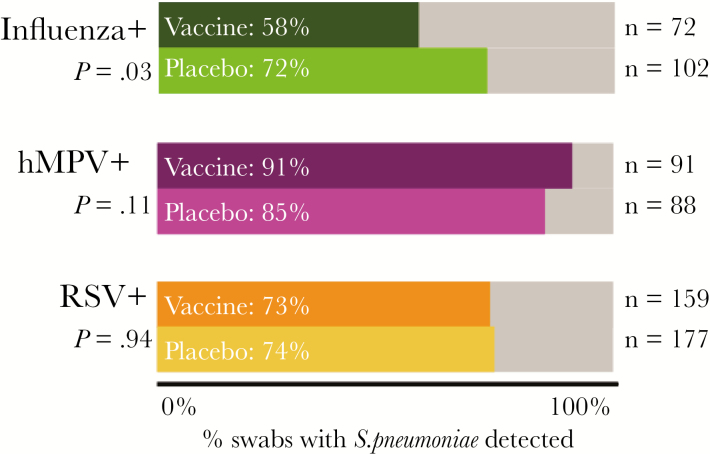
Figure 1.
Nasopharyngeal pneumococcal carriage status in infants with respiratory illness in the context of a maternal influenza vaccine trial in Nepal, 2011–2014. Significantly lower rates of pneumococcal carriage were seen in influenza-positive infants of mothers who received the flu vaccine (P = .03, age-adjusted multivariable logistic regression). RSV-positive and hMPV-positive infants served as age-adjusted negative control groups. Abbreviations: hMPV, human metapneumovirus; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; S. pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae.