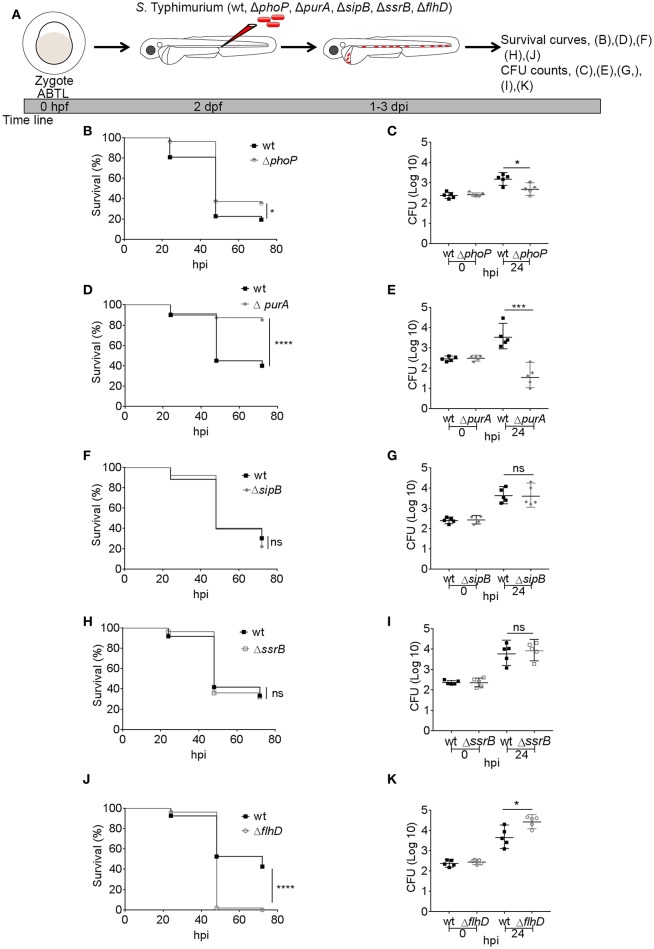
Figure 1.
Comparison of virulence and infection progression of S. Typhimurium mutants. (A) Work flow for experiments followed in (B–K), displayed along the time line of zebrafish development. (B,D,F,H,J) Survival curves for systemically challenged zebrafish with S. Typhimurium mutant strains, ΔphoP (B), ΔpurA (D), ΔsipB (F), ΔssrB (H), and ΔflhD (J) with their respective control groups injected with wild type strain SL1344. One representative of three replicates is shown (n = 50 embryos per group). (C,E,G,I,K) Representative CFU counts of the infections with S. Typhimurium mutant strains, ΔphoP (C), ΔpurA (E), ΔsipB (G), ΔssrB (I), and ΔflhD (K) with their respective control groups injected with wild type strain SL1344 at 24 hpi. One representative of three replicates is shown, where five embryos per time point were used and the log transformed CFU data are shown with the geometric mean per time point. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, ns, non-significant.