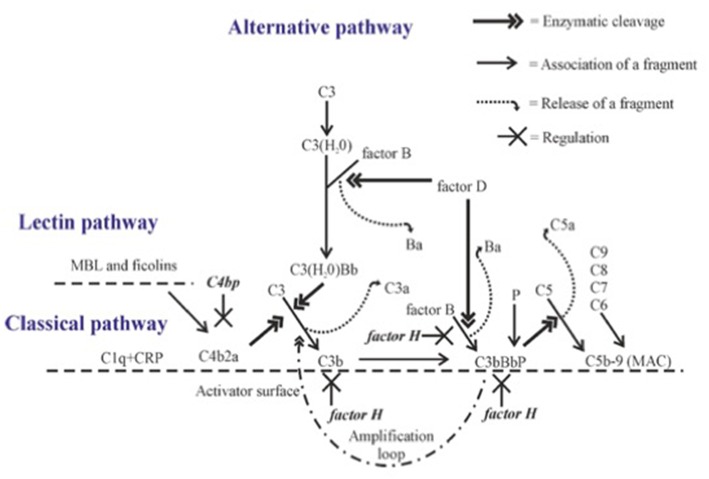
Figure 1.
Complement activation with emphasis on alternative pathway amplification. Complement proteins interact with each other in sequence leading to cleavage of C3 to C3b. Activation on a suitable target leads to opsonization (coating with C1q, C4b, C3b, or iC3b), release of chemotactic and anaphylatoxic fragments (C5a, C3a) and formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC). C4bp inhibits the CP C3 convertase C4b2a. The alternative pathway gets amplified, when C3 convertase (C3bBb) activates additional C3 molecules by cleavage to C3b to generate new C3 convertase enzymes. This amplification step efficiently opsonizes the target with C3b molecules and its inactivation fragment iC3b. Factor H is the main inhibitor of the amplification loop. Its function is to promote C3b inactivation, inhibit binding of factor B to C3b and accelerate the dissociation of the AP C3 convertases.