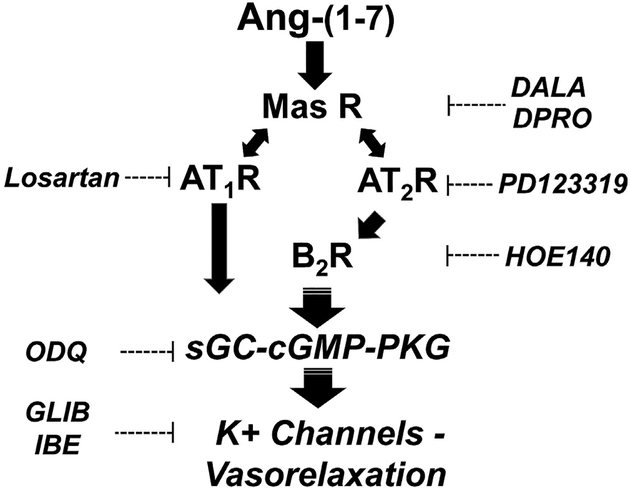
Fig. 6.
Potential scheme for the interaction of Ang-(1–7) with angiotensin receptors to elicit vasorelaxation of renal artery. Ang-(1–7) binds to the Mas receptor to increase cGMP and induce vasorelaxation via activation of K+ channels. The Mas receptor (Mas R) antagonists [D-Ala7]-Ang-(1–7) (DALA) and [D-Pro7]-Ang-(1–7) (DPRO) directly block the binding of Ang-(1–7) within the endothelium. Ang-(1–7) stimulation of the Mas R subsequently activates the AT1 and AT2 R through an unknown mechanism. Ang-(1–7) activation of the kinin B2 receptor (BK2 R) via the AT2R may increase cGMP levels by the stimulation of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) that subsequently leads to activation of protein kinase G (PKG) and K+ channels within the vascular smooth muscle. The K+ channels inhibitors glibenclamide (GLIB) and iberiotoxin (IBE) partially block the vasorelaxant effects of Ang-(1–7). The AT1R, AT2R and BK2R antagonists Losartan, PD123319 and HOE140, respectively block the vasorelaxant effects of Ang-(1–7), as well as the sGC inhibitor ODQ.