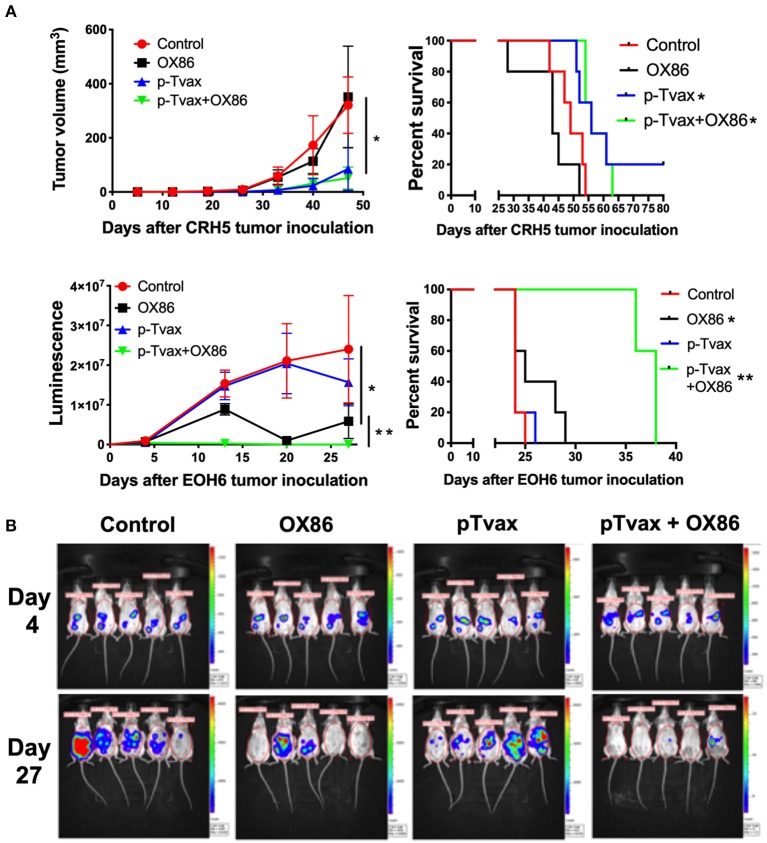
Figure 4.
Combination of p-Tvax vaccine and OX40 agonists delays tumor growth and improves survival in subcutaneous and intraperitoneal mouse models of MM. (A) BALB/c mice were injected s.c. with 5 × 104 CRH5 MM cells, or i.p. with 2 × 105 EOH6 MM cells expressing luciferase. Seven and 14 d after tumor injection, mice were vaccinated with a s.c. injection of p-Tvax peptides. CpG adjuvant was injected at days 5 and 12, while 200 μg of OX86 was injected at day 9 and 14. Tumor volumes are showed on the left and animal survivals on the right for mice injected with CRH5 (Top) and EOH6 (Bottom). Tumor volumes were measured weekly with a caliper for s.c. tumors. I.p. MM dimensions were assessed by measuring luciferase activity with IVIS imaging following injection with luciferin substrate. Statistical significance between unvaccinated controls and single treatment (*) as well as between single and combination treatments (**), was determined by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test (*p < 0.05, n = 5). For survival, mice were followed until s.c. CRH5 tumors reached volumes of 300 mm3 and were then sacrificed. In i.p. models with EOH6 MM cells, survival was assessed by euthanizing mice at first sign of morbidity. Log-rank analysis was used to determine significance between control and single treatment (*), and between single and combination treatments (**) (p < 0.05, n = 5). (B) Representative images from IVIS tumor dimension analysis of mice carrying EOH6 tumors, vaccinated with the different immunotherapies.