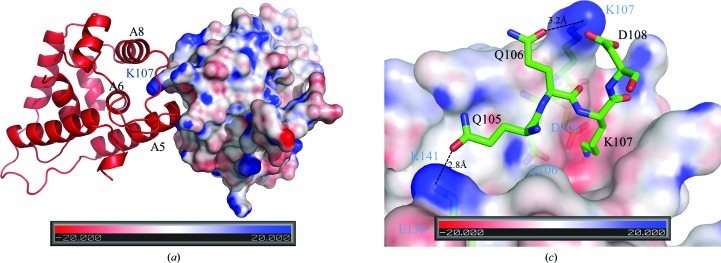
Figure 5.
The dimerization interface of ScHsp104NTD. (a) Within the ScHsp104NTD homodimer, monomer A is shown as a red ribbon drawing and monomer B is shown as a surface-potential drawing using PyMOL (v.1.3; Schrödinger). Helices A5, A6 and A8 of monomer A which are involved in forming the putative peptide-binding groove are labeled in black. The C-terminal end of A5 docks into the peptide-binding groove of monomer B. The protruding Lys107 from monomer B is buried in the peptide-binding groove of monomer A and is labeled in blue. In this figure, the twofold axis lies vertically to the paper and points towards the reader. (b) In this figure, Gln105, Gln106, Lys107 and Asp108 of monomer A of the ScHsp104NTD homodimer are shown in stick mode and labeled in black. Monomer B is shown as a surface-potential drawing. Gln106, Lys107, Asp108 and Lys141 of monomer B are shown in stick mode under the semi-transparent surface and are labeled in blue. The hydrogen bonds between Gln105 and Gln106 from monomer A and Lys141 and Lys107 from monomer B are shown as dotted lines.