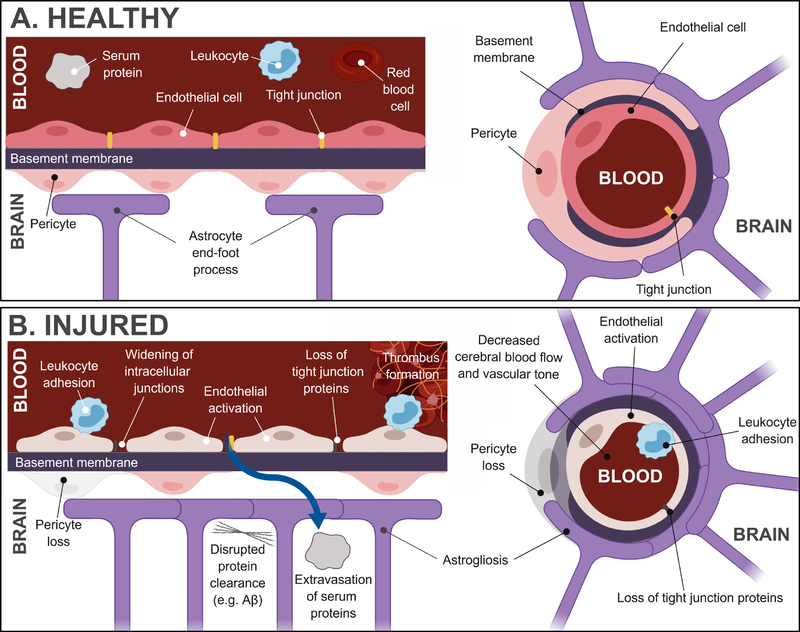
Figure 1: Healthy and injured neurovascular unit.
A. At the capillary level, the neurovascular unit is composed of endothelial cells, perivascular astrocytes, and pericytes. Smooth muscle cells are present at the artery/arteriole/venule levels (not shown). The endothelial cells form a monolayer consisting of intercellular tight junctions to form the blood-brain barrier. B. Following injury, a number of vascular changes have been reported in preclinical studies, including widening of intracellular junctions, loss of tight junction proteins – both of which contribute to extravasation of serum proteins into the parenchyma – astrogliosis, pericyte loss, endothelial activation, leukocyte adhesion, thrombus formation and disrupted protein clearance.