Fig. 1. Architecture of the AIMNet model.
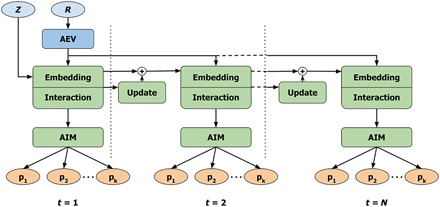
The model uses atomic numbers Z and coordinates R as input features. The coordinates are transformed with ANI-type symmetry functions into AEVs. Atom types are represented with learnable atomic feature vectors (AFV), which are used as embedding vectors for AEVs. The interaction of an atom with its environment produces the AIM representation of the atom used to predict a set of target atom properties {pk}. The environment-dependent update to AFV within N iterations is used to make the embedding vectors for each atom consistent with its environment. Input data are colored in blue, predicted endpoints are in orange, and neural network blocks are in green.
