Figure 2:
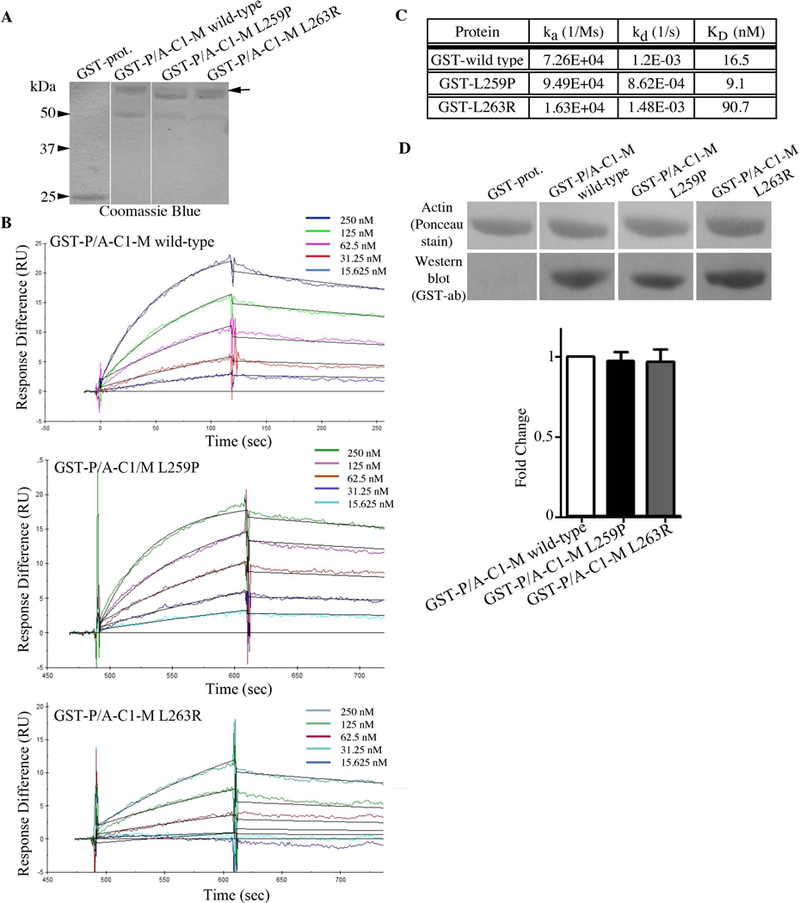
(A) Coomassie blue stained gel showing equivalent amounts (1.5 μg) of control GST, wild-type GST-P/A-C1-M, mutant GST-P/A-C1-M L259P, and mutant GST-P/A-C1-M L263R proteins used in the overlay and Biacore assays. Full length GST-P/A-C1-M recombinant proteins (~58 kDa) are denoted with an arrow; the preparations of both mutant proteins contain a very closely migrating degradation product (56–57 kDa), while a degradation product of ~50 kDa is present in all three protein preparations; non-continuous lanes are separated by a white line. (B) Real time kinetics evaluation of the interaction between wild-type or mutant GST-P/A-C1-M proteins and HMM using a Biacore 3000 SPR biosensor. (C) Kinetic measurements at equilibrium indicated that GST-P/A-C1-M L263R binding to HMM was decreased by ~5.5-fold compared to wild-type levels. (D) Equivalent amounts (3 μg) of purified actin were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and overlaid with 0.5 μg/mL of control GST-protein, wild-type GST-P/A-C1-M, or mutant GST-P/A-C1-M carrying the L259P or L263R mutation. Nitrocellulose membranes (Ponceau stain) and films (Western blots probed with GST-ab) were cropped to only include the area of expected signal. Densitometric quantification of at least three independent overlay/immunoblotting experiments indicated that neither mutation significantly affected binding to actin. Control GST-proteins did not bind actin.
