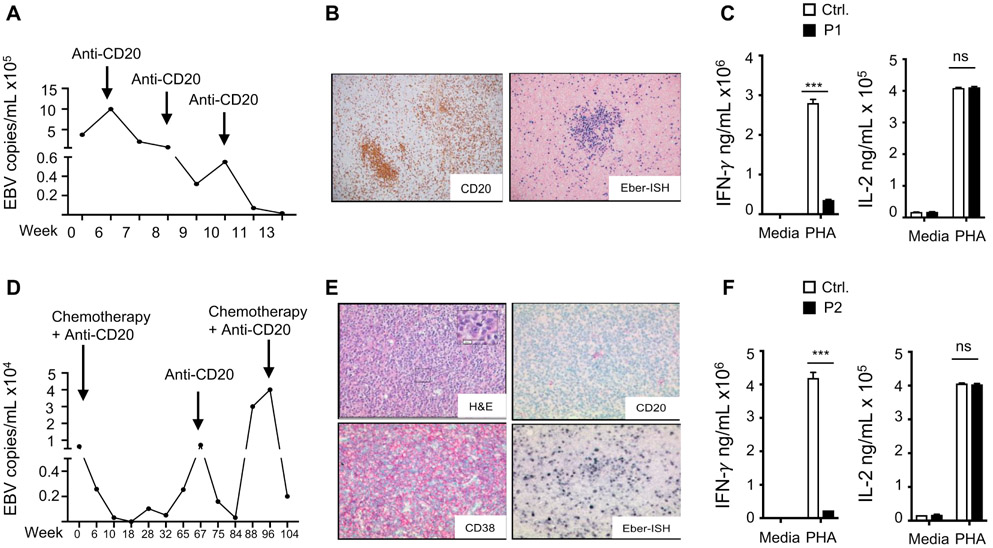
Figure 1. EBV viremia EBV driven lymphoproliferation and impaired IFN-γ secretion in the patients.
A. Circulating EBV viral load in P1. B. Immunohistochemistry of cervical LN from P1 showing a cluster of CD20+ B cells (left) and positive EBV (EBER) in situ hybridization (right) C. IFN-γ and IL-2 levels in supernatants of PHA Stimulated PBMCs from P1 and controls (n=3) in two independent experiments. D. Circulating EBV viral load P2. E. H&E stain of cervical LN from P2 showing a diffuse growth pattern (upper left), and immunohistochemistry showing negative CD20 staining (upper right), positive CD38 staining (lower left) and positive EBV (EBER) in situ hybridization (lower right) consistent with a DLBCL of plasmablastic subtype. F. IFN-γ and IL-2 levels in supernatants of PHA Stimulated PBMCs from P2 and controls (n=3) in two independent experiments. Results represent the mean, columns and bars represent mean + SEM. *** p<0.001, ns= not significant.