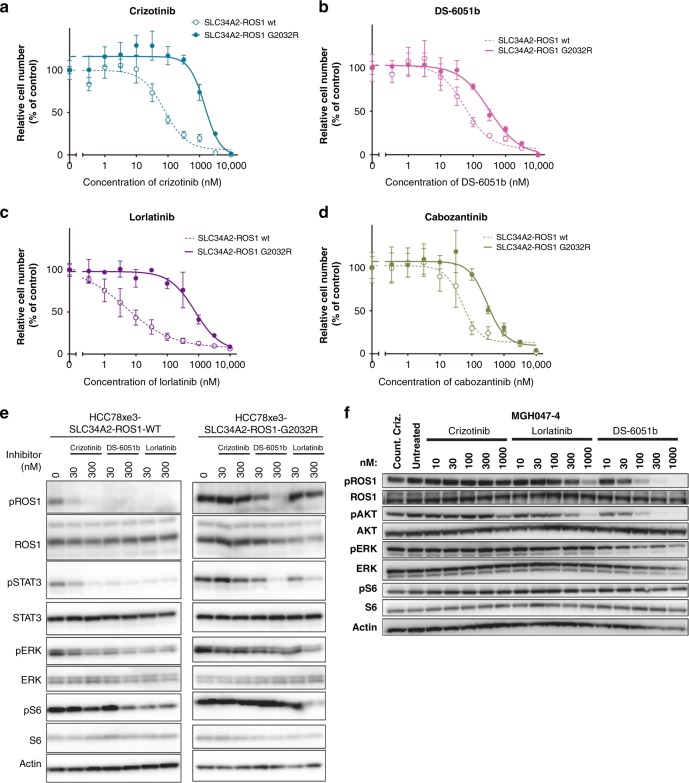
Fig. 5.
DS-6051b effectively inhibited the growth of crizotinib-resistant ROS1-G2032R mutant lung cancer cells. a–d Sensitivity of SLC34A2-ROS1 (WT or G2032R) induced HCC78xe3 cells to crizotinib (a), DS-6051b (b), lorlatinib (c), and cabozantinib (d). The cells were treated with a range of inhibitor doses for 72 h. Cell viability was assessed using CellTiter-Glo assay. e Inhibition of ROS1 phosphorylation by crizotinib, DS-6051b, or lorlatinib in CD74-ROS1 (WT or G2032R) induced HCC78xe3 cells. Both the cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations of the indicated inhibitors for 6 h. The cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect the indicated proteins. f Inhibition of phosphorylation of ROS1 and downstream growth signaling-related molecules by ROS1 inhibitors (crizotinib, lorlatinib, or DS-6051b) in MGH047-4 cells, derived from crizotinib-refractory patients harboring G2032R mutations. The cells were treated with increasing concentrations of the indicated inhibitors for 6 h. The cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect the indicated proteins