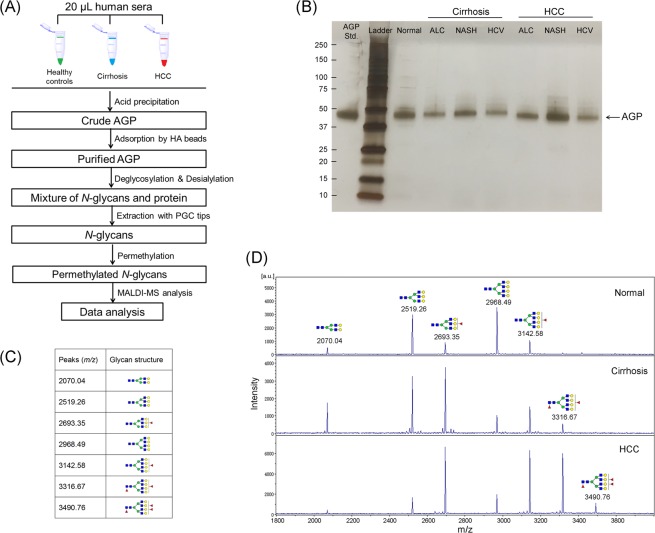
Figure 1.
(A) Workflow of N-glycan profiling of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AGP) derived from sera of healthy controls, liver cirrhosis and HCC. (B) SDS-PAGE image of purified AGP from patient serum in HCC and cirrhosis of different etiologies, i.e. ALC, NASH, and HCV, respectively, with 0.4 μg of an AGP standard protein as a reference. (C) 7 main Desialylated N-Glycans of serum AGP identified in this study. (D) Representative MALDI-TOF MS spectra of desialylated N-glycans in serum AGP derived from healthy controls and patients with liver cirrhosis and HCC, respectively. The bifucosylated tetra-antennary glycan (m/z 3316.67) was highly elevated in HCC and cirrhosis compared to normal subjects. The trifucosylated tetra-antennary glycan (m/z 3490.76) was predominantly identified in HCC patients but was absent in normal subjects and the majority of cirrhosis samples. (The symbols used in the structural formulas as: red triangle, Fuc; blue square, GlcNAc; green circle, Man; yellow circle, Gal).