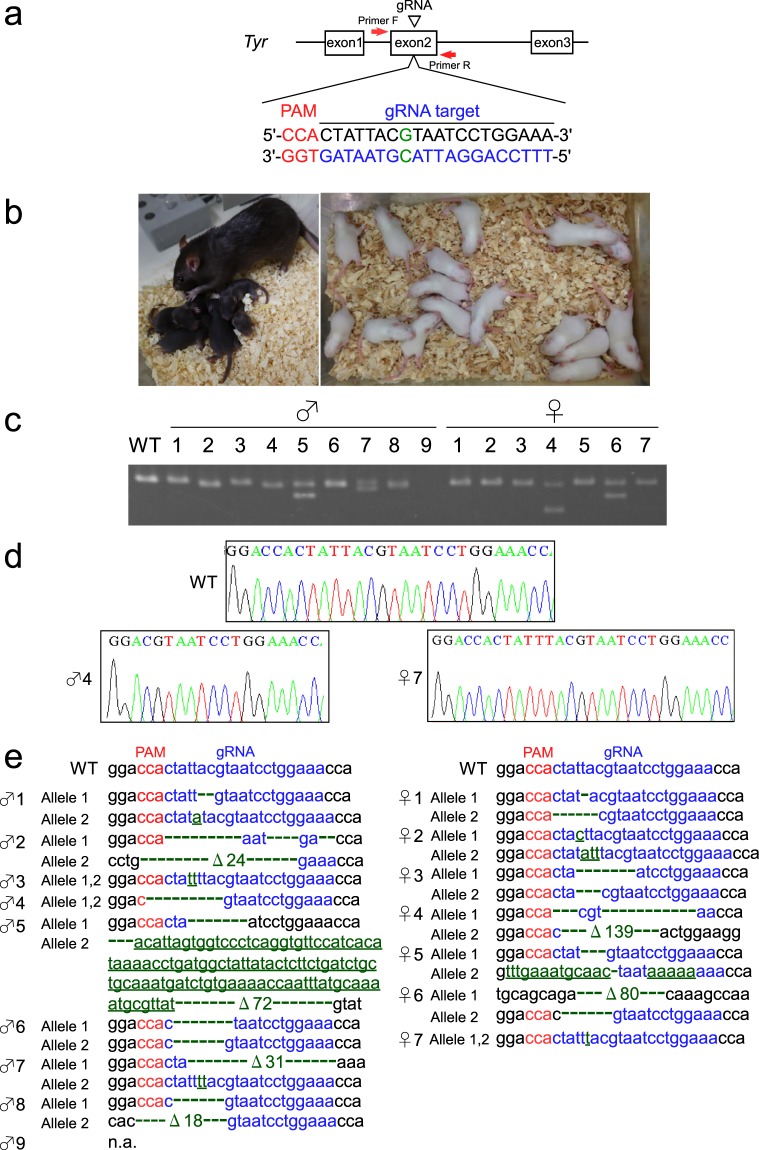
Figure 2.
(a) Schematic representation of the Tyr locus. The target sequence of Tyr exon 2 recognized by gRNA is overlined and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence is marked in red. The target nucleotide ‘G’ marked in green is a key nucleotide for tyrosinase activity, and nucleotide replacement at this position often leads to an albino phenotype. PCR primers used to evaluate the indel mutations around the target site are indicated as red arrows. (b) BN offspring obtained after electroporation of CRISPR/Cas9 complex in IVF embryos. By contrast with the normal (dark brown) BN rats (left panel), all of the offspring obtained had the albino phenotype (right panel). (c) PCR products amplified from genomic DNA of offspring with the albino phenotype represented in (b) showed a wide variety of band patterns. (d) Representative Sanger sequencing at the gRNA target site of male-4 (♂ 4) and female-7 (♀ 7). (e) Sequence analysis of PCR products amplified from the genomic DNA of offspring with the albino phenotype represented in (b). All of the sequences examined contained a wide variety of biallelic indel mutations (green). Insertions are underlined. n.a.: not amplified due to problems with PCR.