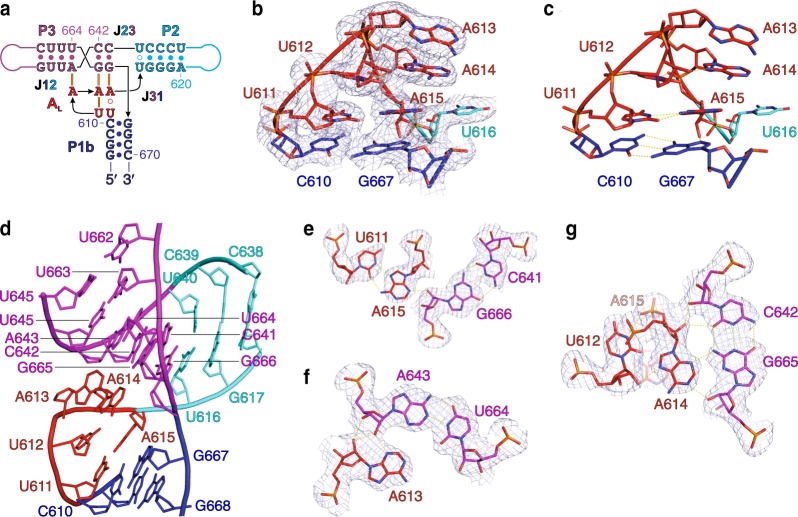
Fig. 4.
Structure of the AL and organization of the three-way junction. a Overall secondary structure of the AL and the three-way junction. Solid and hollow circles depict canonical and non-canonical base-pairing interactions, respectively, and orange bars indicate the tertiary interactions. b Structure of the AL and c interactions within the AL. d Structural organization of the three-way junction in which the dinucleotide stack of A613 and A614 from AL interacts with the minor groove of the helix P3. e–g Three base-triples that stabilize the junction involving the AL nucleotides and the minor groove of the helix P3. Dashed lines in c and e–f represent heteroatoms within the hydrogen bonding distance (2.5–3.5 Å). Blue mesh in b and e–g represents the 2|Fo|−|Fc| electron density map at 1σ contour level and carve radius 1.8 Å