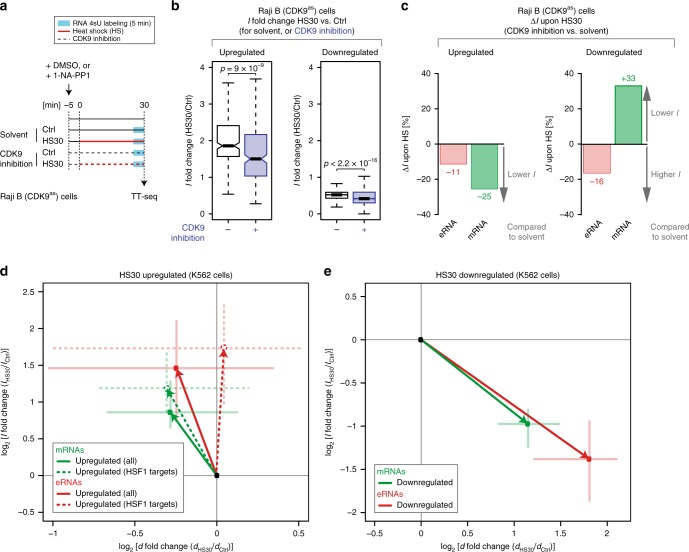
Fig. 4.
Enhancer transcription is generally not pause limited and less dependent on CDK9. a Experimental setup. The adenine analog 1-NA-PP1 allows for rapid and highly specific inhibition of analog-sensitive CDK982 in CRISPR-Cas9 engineered human Raji B (CDK9as) cells28 (Supplementary Fig. 8b–d). CDK9 was inhibited using 5-µM 1-NA-PP1 (CDK9 inhibition) in combination with heat shock at 42 °C for 30 min in human Raji B (CDK9as) cells. DMSO was used as solvent control. b Boxplots of productive initiation frequency I fold change before (in white) and after CDK9 kinase inhibition (in dark blue). Shown are 241 significantly upregulated genes (left boxplot), and 2795 significantly downregulated genes (right boxplot) annotated in Raji B (CDK9as) cells (Supplementary Fig. 9). c ΔI upon upregulation or downregulation between heat shock with CDK9 inhibition (CDK9 inhibited HS30) and heat shock with solvent control (Solvent HS30) is shown in percent [%]. Left: bar plot comparing productive initiation frequency I change (ΔI) with and without CDK9 inhibition for 92 significantly upregulated mRNAs (in green), and 54 significantly upregulated eRNAs (in red) annotated in Raji B (CDK9as) cells. Right: bar plot comparing productive initiation frequency I change (ΔI) with and without CDK9 inhibition for 2210 significantly downregulated mRNAs (in green), and 223 significantly downregulated eRNAs annotated in Raji B (CDK9as) cells. d Log2 fold change of pause duration d and initiation frequency I for 336 significantly upregulated mRNAs (green solid line), and 67 significantly upregulated eRNAs (red solid line) in K562 cells upon 30 min of heat shock (HS30) (Supplementary Fig. 4a). Dashed lines represent HSF1 driven (“Methods”) subsets of 91 mRNAs and 20 eRNAs. e Log2 fold change of pause duration d and initiation frequency I for 1101 significantly downregulated mRNAs (in green), and 99 significantly downregulated eRNAs (in red) in K562 cells upon 30 min of heat shock (HS30) (Supplementary Fig. 4a)