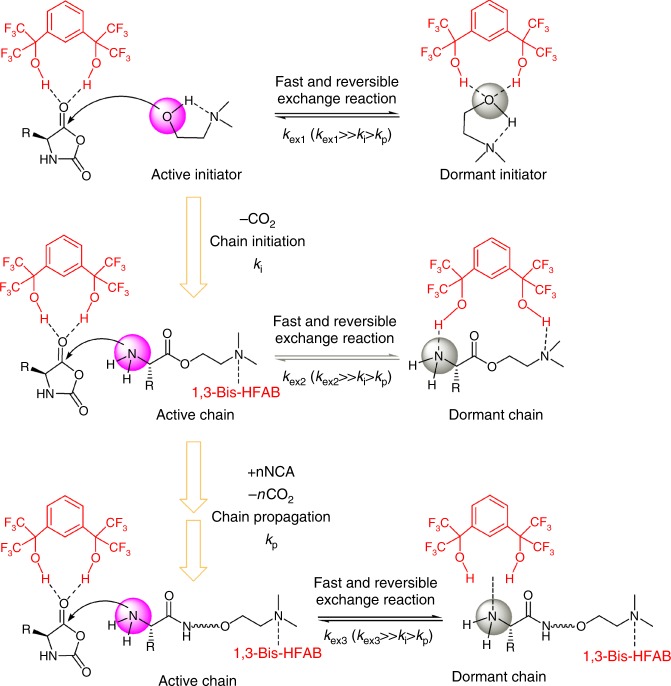
Fig. 7.
Proposed mechanism of ROP of Glu-NCA catalyzed by 1,3-Bis-HFAB. The nucleophilic ring-opening of the NCA by DMEA in the presence of 1,3-Bis-HFAB leads to the initiation of polymerization, whereby the ring-opened NCA releases one carbon dioxide molecule and forms the propagating amine for the subsequent addition of NCA monomers. During polymerization, multiple hydrogen-bonding equilibriums involving NCA monomer, initiator (DMEA), catalyst (1,3-Bis-HFAB), and propagating polymer chain exist. The catalysis proceeds by simultaneous activation of the carbonyl of NCA monomer and dynamic protection of the polymer chain-end amine group via hydrogen bonding to 1,3-Bis-HFAB