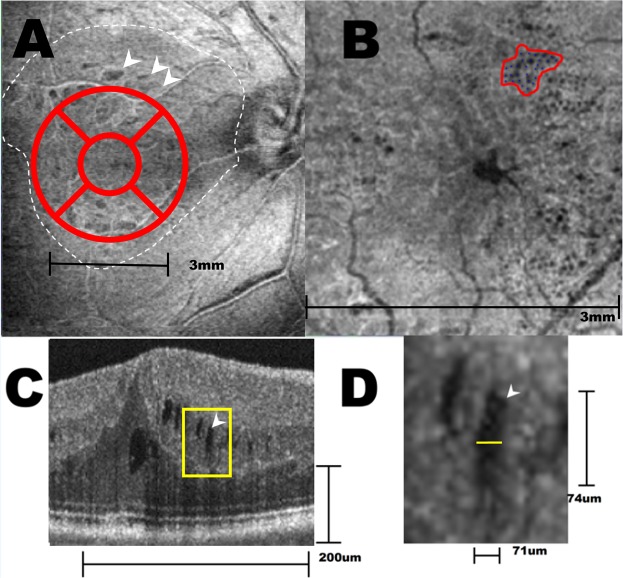
Figure 1.
En face OCT and cross sectional OCT of a right eye that had postoperative microcysts. (A) The central 3 × 3 mm macula was divided into 5 Early Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) areas in this en face image at the superficial capillary plexus level. The center subfield was 1 mm in diameter. The white dotted line indicates the area of ILM being peeled. White arrows indicate dissociated optic nerve fiber layer within the area of denuded ILM. (B) En face view at the deep capillary plexus of the same eye in center 3 × 3 mm of (A) showed microcystic formations in the nasal subfield that extend to the superior and inferior subfields. The area of each cluster and their density of microcyst were calculated as in the irregular circle. (C) In this cross sectional OCT, the microcysts appeared as multiple spindle shaped hollow cavity in the inner nuclear layer. Note that the vertical and horizontal scale lines represent 200 μm. The yellow rectangle area was magnified as shown in (D). (D) The width and length of microcysts determined by a built-in function of the Avanti RTVue XR show that the “spindle-shaped” microcyst actually approximates a spheroid shape (71 × 74 μm) after adjusting the vertical and horizontal scales.