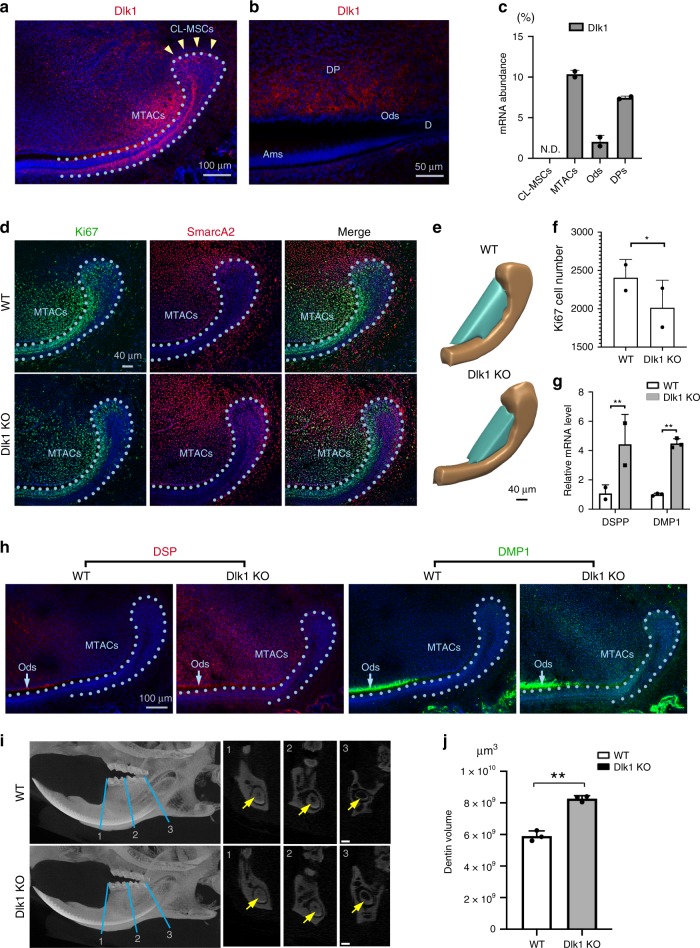
Fig. 6.
Dlk1 prevents MTACs premature differentiation. a, b Immunofluorescence analysis of Dlk1 in the P7 incisor at CL region (a) and labial enamel–dentin differentiation region (b). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Yellow arrowheads and light blue dotted line indicate CL-MSCs and epithelial–mesenchymal junction, respectively. Ams ameloblasts, d dentin, DP dental pulp, Ods odontoblasts. c Real-time RT-PCR analysis of Dlk1 in the indicated laser captured cell populations in the P7 CD1 mouse incisor from n = 5 biologically independent animals. Triplicated samples were used for real time RT-PCR analysis. ND: not detected. d Double immunofluorescence analysis of Ki67 and SmarcA2 in the wild type (WT) and Dlk1 KO mice at P7. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Light blue dotted line indicates CL-MSCs and epithelial–mesenchymal junction. e 3D view of arbitrarily defined a countable MTACs region by aligning the anterior tip of the CL epithelium and first differentiated pre-odontoblasts (also see Fig. 5e). Ki67-positive cells in the cyan regions were quantified in f. f Quantification of Ki67-positive cell number at the cyan region indicated in e, from n = 2 biologically independent animals. Student’s t-test was performed. *p < 0.05. g, h Real-time RT-PCR (g) and immunofluorescence analysis (h) of DSP and DMP1 in the P7 WT and Dlk1 KO mouse incisors. mRNA were extracted from n = 5 biologically independent animals. Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferoni correction was performed. **p < 0.01. Light blue dotted line indicate CL-MSCs and epithelial–mesenchymal junction. i Micro-CT analysis of 2-month-old WT vs. Dlk1 KO mouse lower incisors. Yellow arrows indicate tooth pulp. Yellow arrows indicate dentin layer. j Dentin volume quantification of the 2-month-old WT (n = 3) vs. Dlk1 KO (n = 3) mouse lower incisors. Paired two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. **p < 0.01. Error bars represent standard deviation. Bars: a and h: 100 μm; b: 50 μm; c: 100 μm; d and e: 40 μm; i: 200 μm