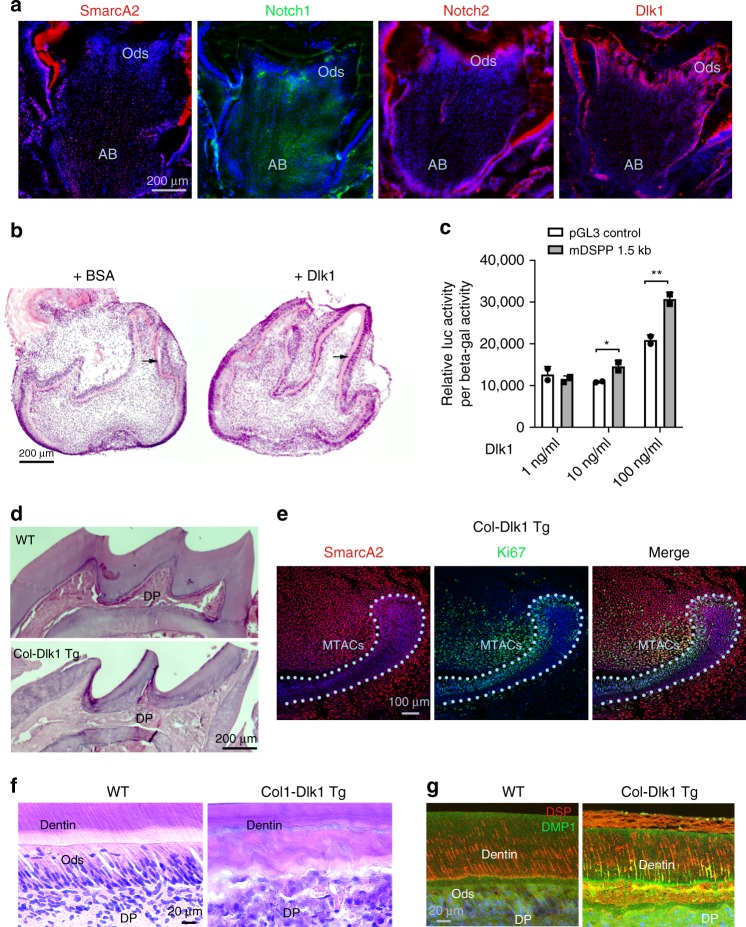
Fig. 8.
Dlk1 can be applied in enhancing MSCs lineage differentiation. a Immunofluorescence analysis of indicated molecules in the P7 CD1 mouse first lower molars. AB apical bud, Ods odontoblasts. b Representative images for organ cultures of E16.5 mouse first lower molar for 4 days in the absence or presence of Dlk1. Black arrows indicate dentin layers. Note the increased deposition of dentin in the Dlk1-treated samples. c Mouse DSPP promoter luciferase analysis in the MO6-G3 cells after receiving Dlk1 treatment at different concentrations. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Genomic DNA were extracted from n = 3 biologically independent samples. Paired Student’s t-test was performed. No asterisk: p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. d H&E images of the upper tooth crowns of the WT vs. Col-Dlk1 Tg mouse first lower molars. Note the mutant mouse’s dental pulp (DP) is fully mineralized. e SmarcA2 and Ki67 double staining on Col-Dlk1 Tg mouse incisor at P7. Light blue dotted lines indicate epithelial–mesenchymal junctions. f, g H&E (f) and immunofluorescence analysis (g) of WT vs. Col-Dlk1 Tg mouse incisor labial dentin and tooth pulp. Error bars represent standard deviation. Bars: a, b and d: 10 μm; e: 100 μm; f, g: 20 μm