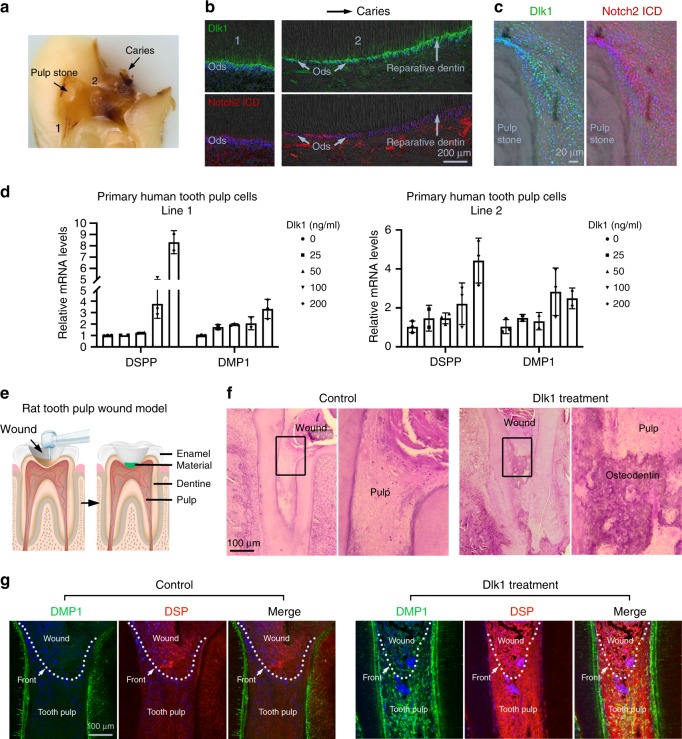
Fig. 9.
A translational strategy of applying Dlk1 in dental regenerative medicine. a Representative cross-sectional view of a human tooth with caries in paraffin- embedded block. Arrows indicate the caries site and a pulp stone in the tooth pulp. 1 indicates a relative healthy region and 2 indicates an adjacent region near the caries. b, c Immunofluorescent analysis of Dlk1 and Notch2 expression in the same sample of a, at different regions of the tooth. Pulp stone images were overlapped with phase contrast images to illustrate the stone location. d DSPP and DMP1 mRNA expression analysis with real-time RT-PCR in two independent human tooth pulp papilla cell lines treated with soluble Dlk1 at indicated concentrations (X axis). mRNA were extracted from n = 3 biologically independent samples. e Schematic illustration of the design of rat molar tooth capping model. f, g Representative H&E (f) and immunofluorescence (g) analyses of the rat molars received capping without (control) and with Dlk1 treatment for 7 days. Samples were immunolabelled for DMP1 and DSP and counterstained with DAPI. White dotted lines mark the wound fronts. Error bars represent standard deviation. Bars: b: 200 μm; c: 20 μm; f, g: 100 μm