Fig. 2.
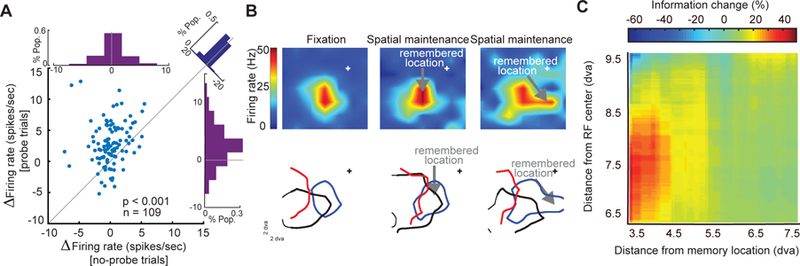
Changes in MT visual sensitivity during WM. (a) During the memory period, visually evoked activity increased, but delay activity in the absence of probes was unchanged. A revised version of MGS task with probe presentation was used; visual probes appeared on 91% of trials, during both the fixation and delay periods of the MGS task. Scatter plot of WM-induced changes in the visually evoked spiking activity (probe trials) against WM-induced changes in the delay period activity (no-probe trials). Top histogram indicates the WM-induced change in delay period activity; right histogram indicates the WM-induced change in visually evoked activity. Diagonal histogram illustrates the difference between the effects of WM on firing rates in the presence and absence of visual probes. (b) RFs shift toward the WM location. Heat map showing the RF of an example MT neuron during fixation (at cross); RF of the same neuron measured while the monkey remembered a location inside of the RF, indicated by the arrow; and RF of the same neuron while the monkey remembered a location to the right of the fixation RF. Lower plots show the RF outlines of three simultaneously recorded MT neurons during fixation (left) and the delay period when the monkey remembered different locations (right). The blue outline is the RF of the neuron shown in upper plot. (c) Visual information encoded in spike phases increases near the memory location. The increase in mutual information during WM depends on the distance between the probes and the RF center or memory location. Color scale shows the change in mutual information (memory – fixation) between the spikes’ phases (αβ) and probe location for pairs of probes. The change is plotted as a function of the probes’ distance from the RF center (y-axis) and distance from the memory location (x-axis). The geometric mean of the two probe positions was used to calculate distances. Adapted from Bahmani et al. (2018) and Merrikhi et al. (2017)
