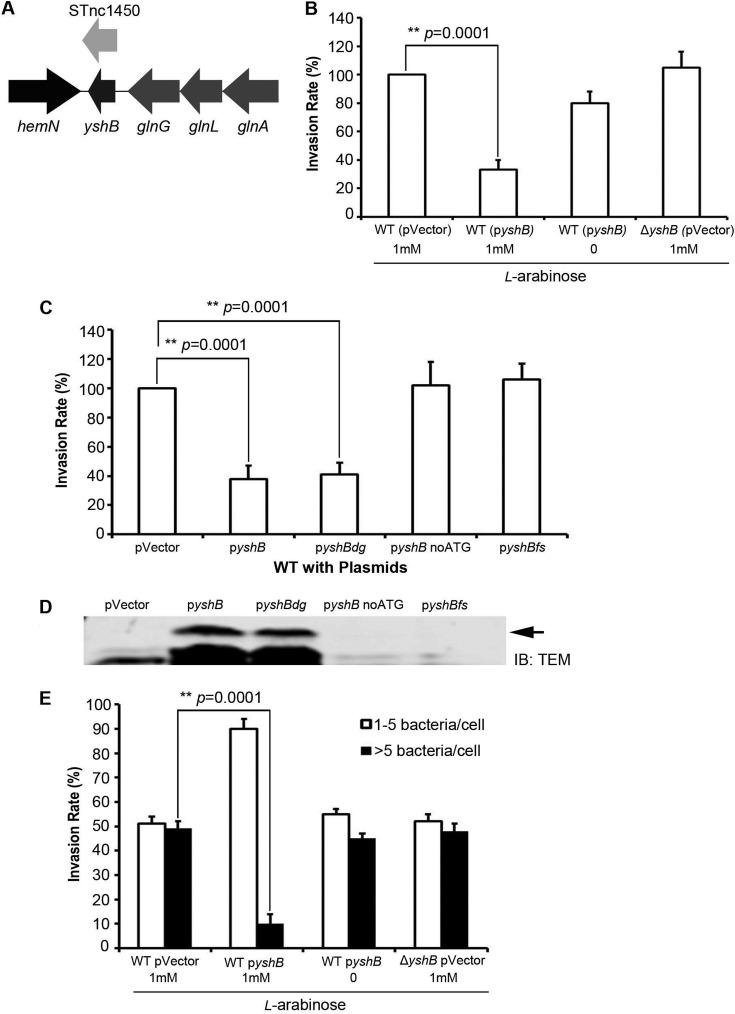
FIG 2.
The small protein YshB within the STnc1450 locus is responsible for the reduced invasion. (A) Genomic location of STnc1450 in S. Typhimurium SL1344, showing the presence of an open reading frame encoding the small protein YshB. (B) Relative invasion rates for Salmonella strains with induced YshB from an arabinose-inducible plasmid (pZP3628) in the wild-type (WT) (SL1344) background, evaluated with the gentamicin protection assay. (C) Relative invasion rates assessed similarly for YshB encoded by degenerate nucleotide sequences (pZP3634), with no start codon (pZP3399), or with frameshifted yshB (pZP3400). (D) Immunoblot showing the expression of YshB from pyshB (pZP3628) and pyshBdg (pZP3634). The bacterial cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-TEM1 antibody. The arrow indicates the 35-kDa YshB-TEM1 fusion protein. (E) Inside/outside differential staining for the wild-type, ΔyshB, and YshB-induced (pZP3628) strains. Percentages of cells with either 1 to 5 or >5 internalized bacteria were enumerated. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences, with the indicated P values. Three independent experiments were carried out, with the means ± standard deviations (error bars) shown.