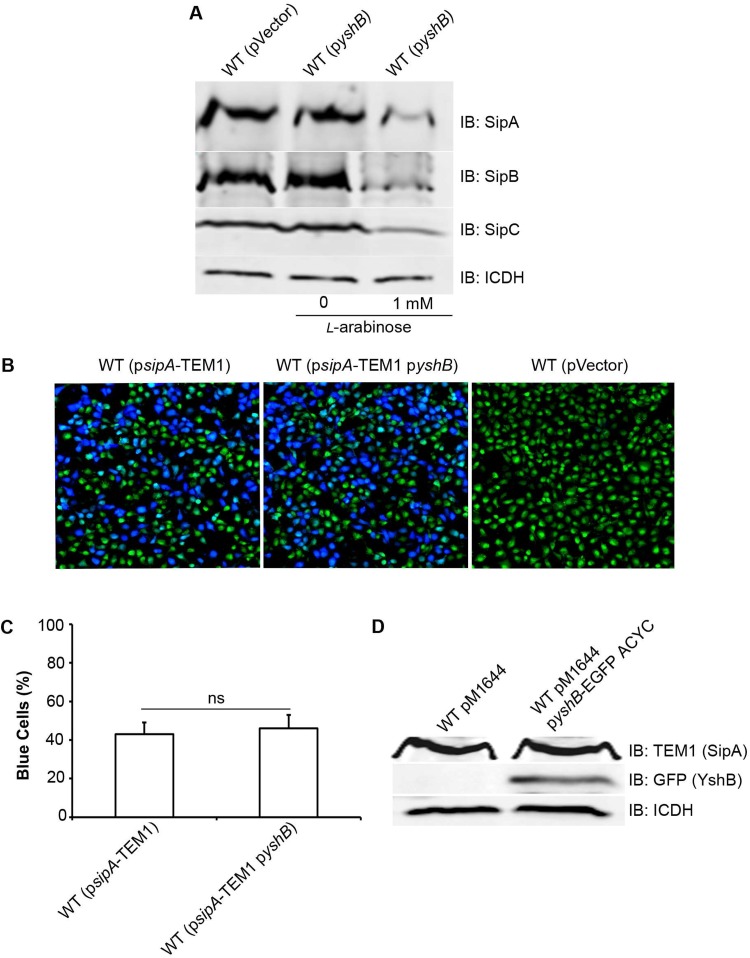
FIG 4.
Induction of YshB reduces the expression of invasion genes. (A) Immunoblot (IB) analysis of bacterial whole-cell lysates for the expression of SipA, SipB, and SipC after growth under SPI-1-inducing conditions, with and without YshB induction (pZP3628). Polyclonal rabbit anti-SipA, anti-SipB, and anti-SipC primary antibodies were used, and rabbit anti-ICDH was used to probe the loading control. (B) β-Lactamase-based translocation assay to assess the translocation efficiency of SipA from pM1644 in YshB-induced (pZP3682) cells. Wild-type (WT) Salmonella strains with pM1644 and plasmid pZP2277, in which the SipA from pM1644 was replaced by the RfA cassette of the Gateway vector conversion system, were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. The translocation efficiency was evaluated by enumerating blue versus green cells under a confocal laser scanning microscope. (C) Percentage of blue cells in panel B, to quantitate the SipA-TEM1 translocation efficiency. Three independent experiments were carried out, and the means ± standard deviations (error bars) are shown. (D) Immunoblot analysis of the bacterial culture used in panel B, showing that SipA expression from pM1644 remains unaffected when YshB is overexpressed (pZP3682).