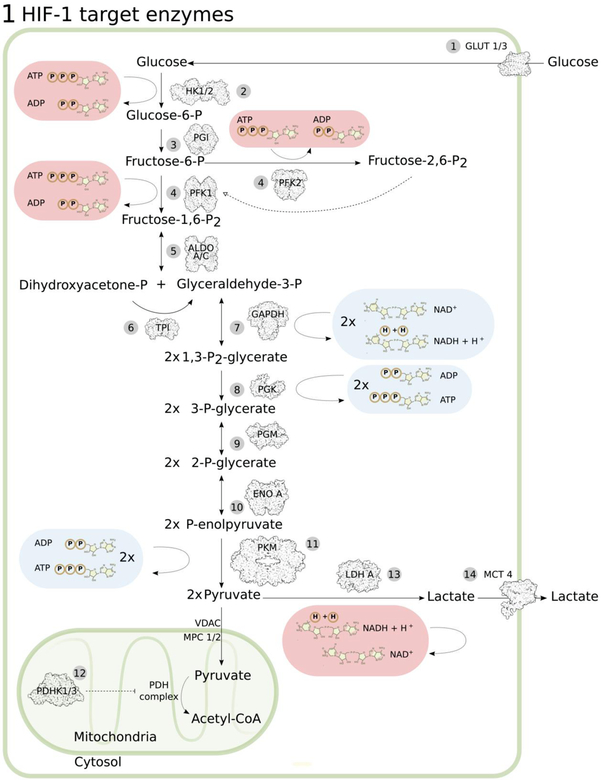
Figure 1: Glycolytic HIF-1 target genes.
(1) GLUT1/3, glucose transporter 1 and 39, 10, 119, (2) HK1/2, hexokinase 1 and 2120, 121, (3) PGI, phosphoglucose isomerase121, 122, (4) PFK1/2, phosphofructokinase 1 and 2121, 123, (5) ALDO A/C, aldolase A and C119, 121, 124, (6) TPI, triosephosphate isomerase121, 125, (7) GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase121, 126, (8) PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase119, 121, 124, (9) PGM, phosphoglycerate mutase121, 127, (10) ENO A, enolase A121, 128, (11) PKM, pyruvate kinase M121, 124, (12) PDHK1/3, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 and 315–17, (13) LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A19, 121, 128, (14) MCT4, monocarboxylate transporter 4129. Pyruvate enters mitochondria through VDAC (voltage-dependent anion channel) in the outer and MPC 1/2 (mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1/2) in the inner mitochondrial membrane, followed by conversion to Acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex in the mitochondrial matrix.