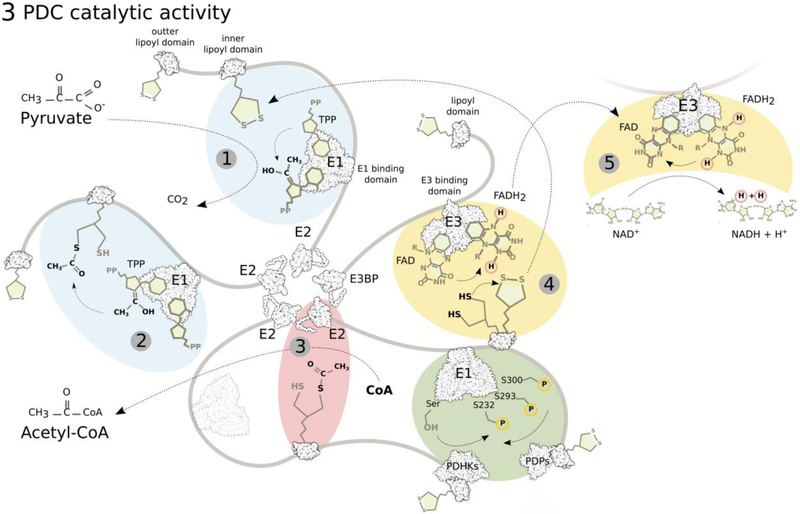
Figure 3: PDC reaction sequence.
E1 (PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase) first catalyzes thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)-dependent irreversible decarboxylation of pyruvate (1) and reductive acetylation of lipoate on the lipoyl domains of E2 (and E3BP), the rate-limiting step (2). E2 (DLT, dihydrolipoyl transacetylase) then catalyzes the transfer of the acetyl group from dihydrolipoate to CoA producing Acetyl-CoA (3). E3 (DLDH, dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase) oxidizes dihydrolipoate back to lipoate by reducing its FAD cofactor to FADH2 (4), which is oxidized back to FAD by NAD+ (5). Movement of the lipoyl domains between active sites of the individual enzymes is executed by the mobile arms of E2 and E3BP.