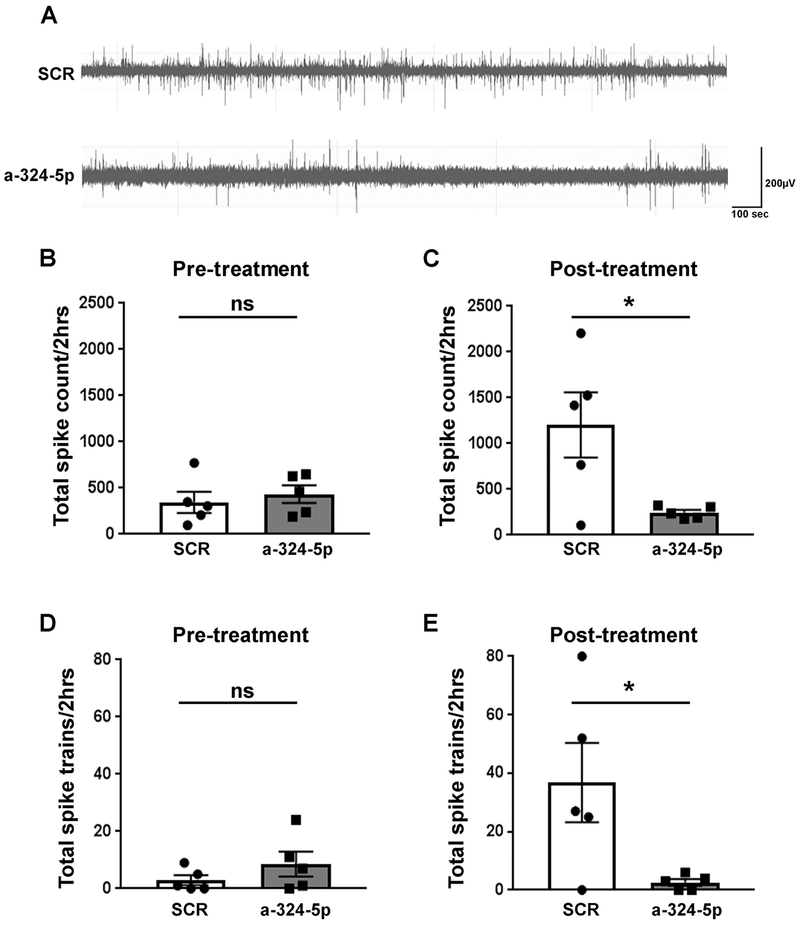
Figure 3: Antagonizing miR-324-5p in vivo reduces the number of interictal spikes and spike trains in epileptic mice.
(A) Representative EEG traces of interictal spikes in scrambled or miR-324-5p antagomir-injected mice. (B,D) Before treatment, no significant differences were observed in total spike count (B, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(8)=0.590, p=0.572) and the number of spike trains (D, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(8)=1.195, p=0.266) between scrambled and miR-324-5p mice (2-hour period over 3 days). (C,E) After treatment, total spike number (C, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(8)=2.676, *p=0.028) and total spike trains (E, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(8)=2.51, *p=0.036) were significantly lower in miR-324-5p-specific antagomir-injected mice compared to the scrambled control (2-hour period over 3 days). Error bars represent SEM, n=5 for both conditions. Also see extended EEG trace in Fig. S6.