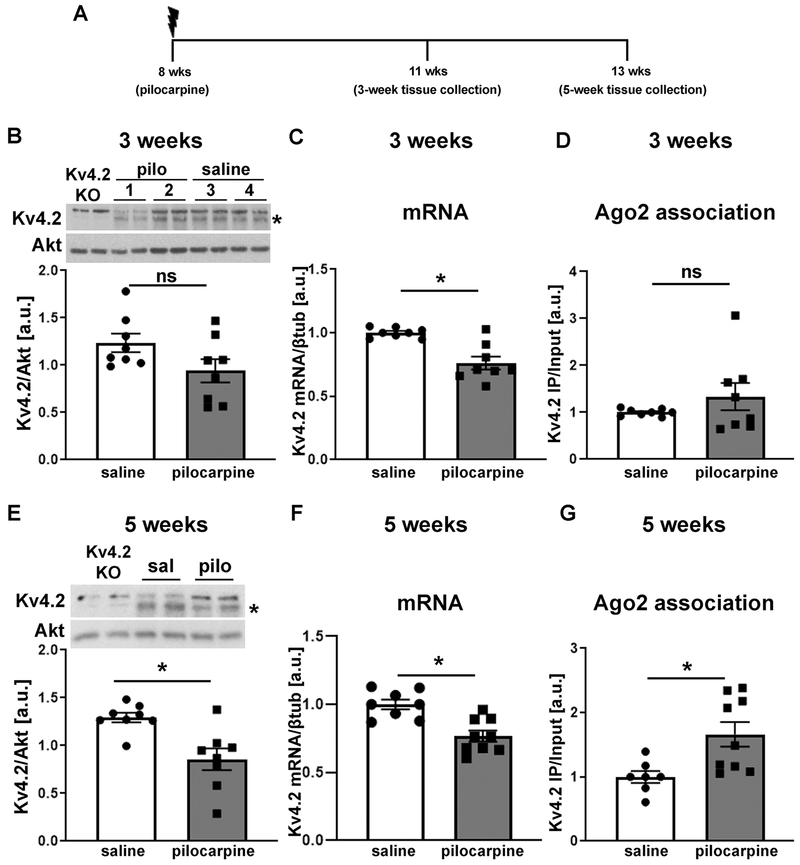
Figure 6: MicroRNA-induced silencing of Kv4.2 is increased in epileptic mice.
(A) Timeline depicting age of mice during pilocarpine injection and tissue collection. (B-D) Three weeks after pilocarpine injection, when mice start to develop spontaneous seizures, no significant reduction in Kv4.2 protein levels (B: n=8, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(14)=1.899, p=0.078) or Kv4.2 mRNA association with Ago2 (i.e. the RISC) (D: n=8, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(14)=1.168, p=0.262), but significantly reduced Kv4.2 mRNA (C: n=8, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(14)=4.470, *p<0.001) was observed. (E-G) Five weeks following pilocarpine treatment, when mice have frequent spontaneous seizures, significantly reduced Kv4.2 protein (E: n=8, unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(14)=3.513, *p=0.003) and mRNA levels (F: saline: n=8, pilo: n=9; unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(15)=4.218, *p<0.001), and significantly increased association of Kv4.2 mRNA with Ago2 (G: saline: n=7, pilocarpine: n=9, two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, *p=0.008) compared to saline control was observed. Example western blots for B and E are shown at top (samples loaded in duplicates), Kv4.2-specific signal was normalized to Akt on the same blot. Asterisk indicates Kv4.2-specific band that is absent in lysates from Kv4.2 KO mice. Total mRNA levels in C and F were quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to βtubulin. mRNA levels in Ago2-IPs in D and G were quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to input levels. Error bars represent SEM.