Figure 5.
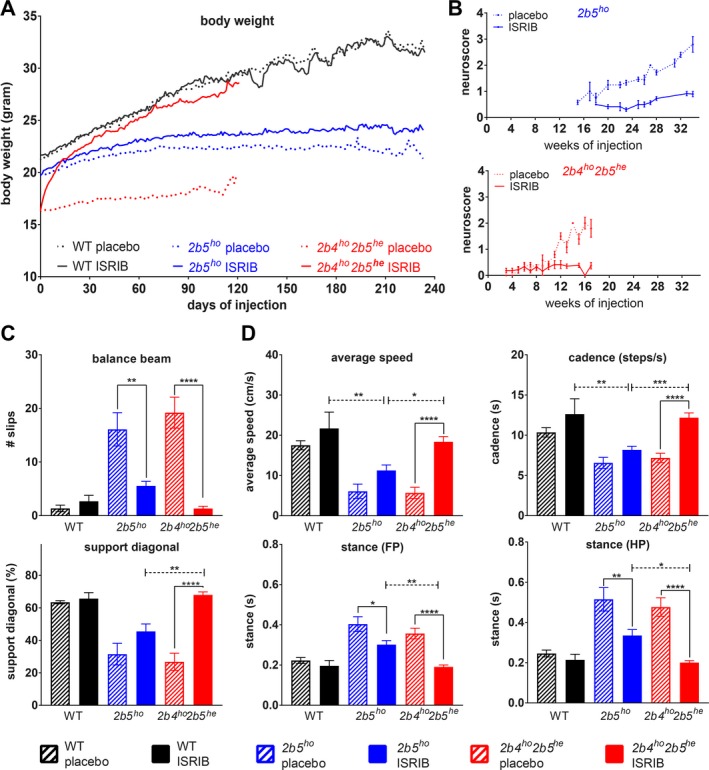
ISRIB ameliorates clinical signs in two VWM mouse models, most effectively in 2b4ho2b5he mice. Mice were injected daily with vehicle or 1 mg/kg ISRIB from an age of 6–8 weeks onwards. (A–D) Graphs show phenotypic measures of placebo‐ and ISRIB‐treated WT (n = 6 per condition) and VWM mice (2b5ho and 2b4ho2b5he n = 14 per condition or as indicated): average body weight of WT and VWM mice (A), average neuroscore in VWM mice (B), average number of slips on balance beam (2b5ho n = 11 for placebo, n = 13 for ISRIB and 2b4ho2b5he n = 10 for placebo and n = 13 for ISRIB, (C), average measures of selected CatWalk parameters (2b5ho n = 9 for placebo, n = 13 for ISRIB and 2b4ho2b5he n = 12 for placebo and n = 14 for ISRIB, (D). Error bars indicate SD (graph b), SEM (graphs in c, d), or are left out (graph in a) to allow visualization of the mean values (SEM is shown in Data S6). Raw data of all CatWalk parameters are given in Data S6. Statistical analysis investigating the ISRIB differences in WT, 2b5ho and 2b4ho2b5he was performed with a two‐way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction (Data S6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
