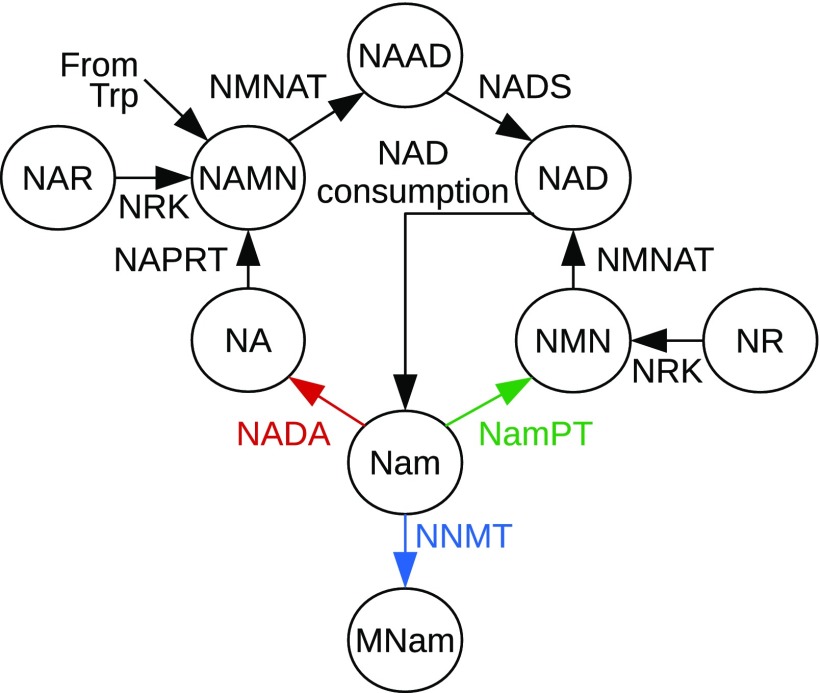
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of NAD biosynthesis pathways. NAD can be synthesized from tryptophan (Trp), Nam, NA, and the corresponding ribosides NR and NA riboside (NAR). Nam is the main precursor in humans and also the product of NAD-consuming signaling reactions by enzymes such as sirtuins (NAD-dependent deacylases) or PARPs. For the recycling of Nam, 2 different pathways exist. The pathway found in yeast, plants, and many bacteria starts with the deamidation of Nam by NADA. Further biosynthesis via the Preiss–Handler pathway, which also exists in vertebrates, requires 3 subsequent enzymatic steps catalyzed by NAPRT, NMNAT, and NADS. In vertebrates, Nam is directly converted to NMN by NamPT. The NNMT degrades MNam, which, in mammals, is excreted with the urine. The color code for the 3 different enzymes utilizing Nam is used in subsequent figures to denote the presence of these enzymes in different organisms.