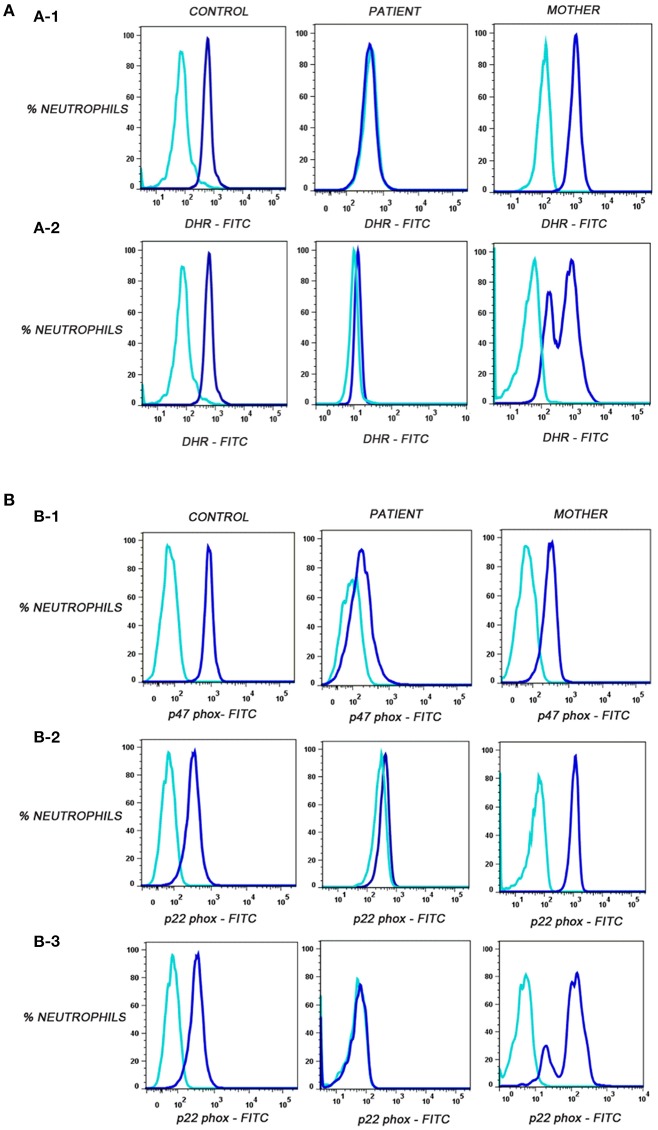
Figure 1.
(A) Flow cytometric evaluation of dihydrorhodamine-123 (DHR) assay on neutrophils in control, corresponding mother (to distinguish XL-CGD from autosomal CGD patient), and CGD patients. Unstimulated neutrophils (sky blue) showed no oxidation of dihydrorhodamine-123 (DHR) reagent to rhodamine in contrast to stimulated neutrophils (blue) by PMA. (A-1) Oxidation of DHR in patient P1 representative of autosomal recessive CGD(P1,P2,P3)/de novo X-linked CGD (P5) patient, control, and mother's sample. (A-2) Oxidation of DHR in patient P4-X-linked CGD patient, carrier mother, and control sample. (B) Flow cytometric evaluation of p47phox and p22phox expression on neutrophils. Median fluorescent intensities were recorded for stained (blue) and unstained (sky blue) neutrophils in control, patient, and mother's sample. (B-1) Defective p47phox component expression in patient P1, control, and mother. (B-2) Defective p22phox component expression in patient P5, control, and mother*. (B-3) Defective p22phox component expression in patient P4, control, and mosaic pattern in mother clearly indicating X-linked defect (gp91phox defect) in patient P4. *Important to further confirm by molecular characterization in patient and parents.