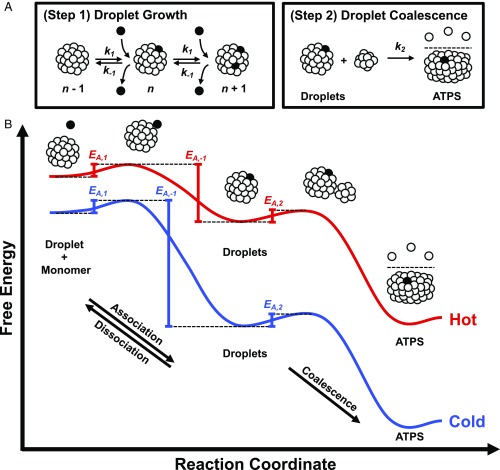
Fig. 7.
Two-step mechanism for ATPS formation. (A) ATPS formation begins with droplet growth (Step 1 in A) involving the sequential, reversible association of protein monomers with protein-rich droplets, characterized by the association, k1, and dissociation, k−1. The circles represent folded protein monomers, several of which have been colored in black to highlight the growth mechanism. The number of monomers in the droplets, n, are not drawn to scale. The final stage of ATPS formation is the irreversible coalescence of droplets (Step 2 in A), characterized by the coalescence rate constant, k2. (B) The reaction coordinate diagrams for ATPS formation at hot (red curve) and cold (blue curve) temperatures relate the apparent activation energies measured in Fig. 4B to the 2-step mechanism in A. The activation energies for the elementary steps are not drawn to scale in B.