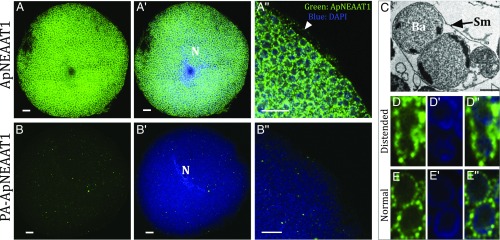
Fig. 3.
Immunolocalization of ApNEAAT1 to the symbiosomal and bacteriocyte membranes of isolated bacteriocyte cells. (A) Immunolocalization of ApNEAAT1 (green) reveals extensive punctate staining around individual Buchnera cells. (A′) Merge of the anti-ApNEAAT1 image and DAPI-stained nuclear and Buchnera DNA (blue). (A″) Magnified region of bacteriocyte cell showing merge of anti-ApNEAAT1 localization (green) and DAPI-stained DNA (blue), arrowhead marks localization to the bacteriocyte cell membrane. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (B–B″) Comparable control experiments were performed with isolated A. pisum bacteriocytes with peptide preadsorbed (PA) anti-ApNEAAT1 antibody. The secondary antibody was Alexa-Fluor 568 donkey anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) (Scale bars, 10 μm). N, bacteriocyte cell nucleus. (C) TEM of distended symbiosomal membrane (Sm) enclosing 2 B. aphidicola (Ba). (Reprinted from ref. 59, with permission from Elsevier.) Left to right: (D) Immunolocalization of ApNEAAT1 to the distended symbiosomal membrane; (D′) DAPI-stained Buchnera cells; (D″) merge of the anti-ApNEAAT1 image (green) and DAPI-stained Buchnera DNA (blue). (E–E″) Comparable images of 2 Buchnera surrounded by their own symbiosomal membranes. For all images, a single representative confocal plane is shown for 3 replicated localization experiments (SI Appendix, Fig. S2).