Two N′-(1-(phenylethylidene)-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazides containing –OH and –OCH3 at the para-position of the phenyl ring have been synthesized and their molecular and crystal structures are reported.
Keywords: crystal structure, acetohydrazides, thiophene, Hirshfeld analysis
Abstract
The synthesis, spectroscopic data, crystal and molecular structures of two N′-(1-phenylbenzylidene)-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazides, namely N′-[1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide, C13H10N2O2S, (3a), and N′-[1-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide, C14H14N2O2S, (3b), are described. Both compounds differ in the substituent at the para position of the phenyl ring: –OH for (3a) and –OCH3 for (3b). In (3a), the thiophene ring is disordered over two orientations with occupancies of 0.762 (3) and 0.238 (3). The configuration about the C=N bond is E. The thiophene and phenyl rings are inclined by 84.0 (3) and 87.0 (9)° for the major- and minor-occupancy disorder components in (3a), and by 85.89 (12)° in (3b). Although these dihedral angles are similar, the conformation of the linker between the two rings is different [the C—C—C—N torsion angle is −ac for (3a) and −sc for (3b), while the C6—C7—N9—N10 torsion angle is +ap for (3a) and −sp for (3b)]. A common feature in the crystal packing of (3a) and (3b) is the presence of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, resulting in the formation of chains of molecules running along the b-axis direction in the case of (3a), or inversion dimers for (3b). The most prominent contributions to the surface contacts are those in which H atoms are involved, as confirmed by an analysis of the Hirshfeld surface.
Chemical context
Acetohydrazides are considered to be good candidates for different pharmaceutical applications, including their use as antibacterial, antifugal, antimicrobial and anticonvulsant agents (Yadav et al., 2015 ▸; Bharti et al., 2010 ▸; Loncle et al., 2004 ▸; Papakonstantinou-Garoufalias et al., 2002 ▸). Moreover, many of them have shown analgesic and antiplatelet properties (Wardakhan et al., 2013 ▸). Combinations of acetohydrazide with other heterocyclic rings have also been investigated, such as the hydrazide-based 2-oxonicotinonitrile derivatives that are considered to be potential antimicrobial agents (El-Sayed et al., 2018 ▸).
As a continuation of our research (Nguyen et al., 2016 ▸; Vu et al., 2016 ▸, 2017 ▸) on the chemical and physical properties of novel polythiophenes, a new thiophene monomer-containing acetohydrazide has been prepared. We have synthesized two N′-(1-(phenylbenzylidene)-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazides and present here the spectroscopic data and crystal structures of the title compounds, together with the Hirshfeld surface analysis.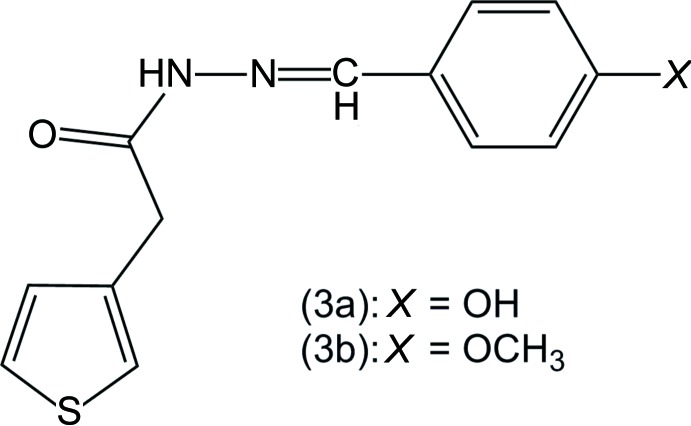
Structural commentary
The hydroxy derivative (3a) crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pbca. The thiophene ring is disordered over two sites (the major and minor components are labelled with the suffixes A and B, respectively), corresponding to a rotation about the C3—C6 bond of approximately 180° with population parameters 0.762 (3) for S1A/C1A–C5A and 0.238 (3) for S1B/C1B–C5B (Fig. 1 ▸). The configuration of the C11=N10 bond can be described as E [the N9—N10—C11—C12 torsion angle is 174.82 (16)°]. The torsion angle C7—N9—N10—C11 of 177.10 (18)° indicates that the conformation around the N9—N10 bond is +ap. The molecule is twisted about the C6—C7 bond with a dihedral angle of 84.0 (3)° between the thiophene and benzene rings [87.0 (9)° for S1B/C1B–C5B] .
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of (3a), with atom labels and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The minor-disorder component is shown in light green.
The methoxy derivative (3b) (Fig. 2 ▸) crystallizes in the triclinic space group P
 . Compared to (3a), the central part of (3b) displays a similar +ap conformation around the N9—N10 bond and an E configuration of the C11=N10 bond, as illustrated by the torsion angles C7—N9—N10—C11 [177.8 (2)°] and N9—N10—C11—C12 [179.26 (19)°]. However, the conformation about the two other bonds, C6—C7 and especially C7—N9, in the linker between both rings is different. The torsion angle C3—C6—C7—N9 is −101.8 (2)° (or -ac) for (3a) and −85.4 (3)° (or -sc) for (3b). As a consequence, in (3b) a short C6—H6⋯N10 interaction occurs (Table 2 ▸). In (3a) we observe an +ap conformation [torsion angle C6—C7—N9—N10 is 167.45 (16)°], while this is -sp in (3b) [torsion angle C6—C7—N9—N10 is −5.8 (3)°]. The dihedral angle between the thiophene and phenyl rings is 85.89 (12)°, in the same order as for (3a).
. Compared to (3a), the central part of (3b) displays a similar +ap conformation around the N9—N10 bond and an E configuration of the C11=N10 bond, as illustrated by the torsion angles C7—N9—N10—C11 [177.8 (2)°] and N9—N10—C11—C12 [179.26 (19)°]. However, the conformation about the two other bonds, C6—C7 and especially C7—N9, in the linker between both rings is different. The torsion angle C3—C6—C7—N9 is −101.8 (2)° (or -ac) for (3a) and −85.4 (3)° (or -sc) for (3b). As a consequence, in (3b) a short C6—H6⋯N10 interaction occurs (Table 2 ▸). In (3a) we observe an +ap conformation [torsion angle C6—C7—N9—N10 is 167.45 (16)°], while this is -sp in (3b) [torsion angle C6—C7—N9—N10 is −5.8 (3)°]. The dihedral angle between the thiophene and phenyl rings is 85.89 (12)°, in the same order as for (3a).
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of (3b) with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (3b) .
Cg1 is the centroid of the S1/C1–C5 thiophene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N9—H9⋯O8i | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.935 (3) | 179 |
| C6—H6A⋯N10 | 0.97 | 2.44 | 2.782 (3) | 100 |
| C13—H13⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.68 | 3.611 (2) | 179 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, molecules of (3a) are connected by N9—H9⋯O8i [symmetry code: (i) −x +  , y +
, y +  , z] hydrogen bonds, resulting in the formation of chains in the b-axis direction with a
, z] hydrogen bonds, resulting in the formation of chains in the b-axis direction with a  (4) graph-set motif (Fig. 3 ▸, Table 1 ▸). In addition, chains with a
(4) graph-set motif (Fig. 3 ▸, Table 1 ▸). In addition, chains with a  (11) graph-set motif running along the a-axis direction are formed by O18—H18⋯O8ii [symmetry code: (ii) x −
(11) graph-set motif running along the a-axis direction are formed by O18—H18⋯O8ii [symmetry code: (ii) x −  , y, −z +
, y, −z +  ] hydrogen bonds (Fig. 4 ▸, Table 1 ▸). Two weaker interactions are present in the packing: a C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π(phenyl) interaction (for details see Table 1 ▸).
] hydrogen bonds (Fig. 4 ▸, Table 1 ▸). Two weaker interactions are present in the packing: a C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π(phenyl) interaction (for details see Table 1 ▸).
Figure 3.
Part of the crystal structure of (3a), showing the chain formation through N—H⋯O interactions (red dashed lines) along the b-axis direction. The minor disorder component is not shown. Symmetry codes: (i) −x +  , y +
, y +  , z; (v) −x +
, z; (v) −x +  , y −
, y −  , z.
, z.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (3a) .
Cg3 is the centroid of the C12–C17 phenyl ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N9—H9⋯O8i | 0.86 | 2.12 | 2.953 (2) | 162 |
| O18—H18⋯O8ii | 0.82 | 1.97 | 2.782 (2) | 169 |
| C2A—H2A⋯O8iii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.439 (7) | 155 |
| C13—H13⋯Cg3iv | 0.93 | 2.89 | 3.818 (3) | 176 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Figure 4.
Part of the crystal structure of (3a), illustrating the chain formation through O—H⋯O interactions (red dashed lines) along the a-axis direction. The minor disorder component is not shown. Symmetry codes: (i) x +  , y, −z +
, y, −z +  ; (ii) x −
; (ii) x −  , y, −z +
, y, −z +  .
.
Replacing the –OH group in (3a) by an –OMe group in (3b) changes the hydrogen-bonding pattern. The crystal packing of (3b) is now characterized by the presence of two different inversion dimers. The first type, with an  (8) graph-set motif, is formed by N9—H9⋯O8i [symmetry code: (i) −x, −y + 2, −z + 1] hydrogen bonds (Fig. 5 ▸, Table 2 ▸). The second one involves C13—H13⋯π(thiophene) interactions (Fig. 6 ▸, Table 2 ▸).
(8) graph-set motif, is formed by N9—H9⋯O8i [symmetry code: (i) −x, −y + 2, −z + 1] hydrogen bonds (Fig. 5 ▸, Table 2 ▸). The second one involves C13—H13⋯π(thiophene) interactions (Fig. 6 ▸, Table 2 ▸).
Figure 5.
A partial packing diagram of (3b), showing dimer formation through N—H⋯O interactions (red dashed lines). Symmetry code: (i) −x, −y + 2, −z + 1.
Figure 6.
A partial packing diagram of (3b), illustrating the dimer formation through C—H⋯π interactions (gray dashed lines). Cg1 is the centroid of the S1/C2–C5 thiophene ring. Symmetry code: (ii) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1.
No voids or π–π stackings are observed in the crystal packing of (3a) and (3b).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.40, update of May 2019; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for the central linker between the two rings in the title compound, C—CH2—C(=O)—NH—N=CH—C (Fig. 7 ▸ a), resulted in 137 hits. Histograms of the distribution of the four torsion angles τ1 –τ4 along the linker backbone are shown in Fig. 7 ▸ b–e [the red and green lines depict the torsion angles for title compounds (3a) and (3b), respectively]. The histogram of τ1 reflects a wide spread with a preference for the −ap/+ap conformation, followed by the −sc/+sc conformation and only a few entries in the remaining regions. In the case of torsion angle τ2, two regions are preferred: −ap/+ap [for the majority of the entries and similar to (3a)] and −sp/+sp [similar to (3b)]. Torsion angles τ3 and τ4 show both a narrow spread in the region −ap/+ap.
Figure 7.
(a) Fragment used for a search in the CSD. (b)–(e) Histograms of torsion angles τ1, τ2, τ3 and τ4, respectively. The vertical red and green lines show the torsion angles observed in title compounds (3a) and (3b), respectively.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
The Hirshfeld surface analysis (Spackman & Jayatilaka, 2009 ▸) and the associated two-dimensional fingerprint plots (McKinnon et al., 2007 ▸) were performed using CrystalExplorer (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). The Hirshfeld surfaces of compounds (3a) and (3b) mapped over d norm are given in Fig. 8 ▸.
Figure 8.
The Hirshfeld surface mapped over d norm for (a) compound (3a) in the range −0.6166 to 1.1782 a.u., and (b) compound (3b) in the range −0.5274 to 1.2642 a.u.
The bright-red spots in Fig. 8 ▸ a near atoms O8 and N9 illustrate the N9—H9⋯O8 hydrogen bond, and near atoms O8 and O18 the O18—H18⋯O8 hydrogen bond. The faint-red spots near atoms O8 and H2A, and C11 and H17 refer to short contacts in the crystal packing of (3a). The most significant contributions to the Hirshfeld surface are from H⋯H (30.5%), C⋯H/H⋯C (26.1%), O⋯H/H⋯O (18.6%) and S⋯H/H⋯S (10.7%) contacts.
For compound (3b), the N9—H9⋯O8 dimer formation is viewed as the bright-red spots near atoms O8 and N9 in Fig. 8 ▸ b. The faint-red spots near atoms H19C and H13 are indicative for a short H19C⋯H19C contact and the C13—H13⋯π(thiophene) interaction. The most significant contributions to the Hirshfeld surface are from H⋯H (40.6%), C⋯H/H⋯C (22.2%), O⋯H/H⋯O (15.1%) and S⋯H/H⋯S (12.5%) contacts.
Synthesis and crystallization
The reaction scheme to synthesize the title compounds, (3a) and (3b), is given in Fig. 9 ▸.
Figure 9.
Reaction scheme for the title compounds (3a) and (3b).
Methyl 2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetate (1) and 2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (2) were synthesized according to our previous research (Vu et al., 2017 ▸).
Synthesis of N ′ -[1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide:
Compound (2) (3 mmol) and the appropriate benzaldehyde derivatives (6 mmol) with acetic acid (1.5 mL) in ethanol (20 mL) were refluxed for 5 h. The reaction mixture was cooled down and the solid product was separated by filtration and purified by recrystallization in ethanol to give the compounds (3a) and (3b).
Data for N ′ -[1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a):
White crystals; m.p. 443 K; yield 63%. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3289, 3207 (NH), 3050, 2874 (C—H), 1621 (C=O), 1606 (CH=N), 1511 (C=C). 1H NMR [Bruker XL-500, 500 MHz, d 6-CDCl3, δ (ppm), J (Hz)]: 7.19 (m, 1H, H2), 7.11 (d, 1H, 5 J = 5.0, H4), 7.25 (dd, 1H, 2 J = 3.0, 4 J = 5.0, H5), 4.07 (s, 2H, H6), 9.17 (s, 1H, H8), 7.79 (s, 1H, H9), 7.52 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 H11, H15), 6.87 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 H12, H14), 10.10/10.04 (s, 1H, H16). 13C NMR [Bruker XL-500, 125 MHz, d 6-CDCl3, δ (ppm)]: 122.3/122.4 (C2), 135.3/135.4 (C3), 128.7/128.8 (C4), 125.4/125.8 (C5), 33.6/35.9 (C6), 165.7/171.4 (C7), 146.7 (C9), 143.5 (C10), 128.3/128.6 (C11, C15), 115.6/116.6 (C12,C14), 159.6/159.2 (C13). Calculation for C13H12N2O2S: M [+H] = 260.9 au.
Data for N ′ -[1-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b):
White crystals, m.p. 431 K, yield 53%. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3442, 3112 (NH), 3014, 2950 (C—H), 1706 (C=O), 1617 (CH=N), 1558, 1503 (C=C). 1H NMR [Bruker XL-500, 500 MHz, d 6-CDCl3, δ (ppm), J (Hz)]: 7.22 (m, 1H, H2); 7.12 (m, 1H, H4); 7.26 (dd, 1H, 2 J = 3.0, 5 J = 5.0, H5); 4.11 (s, 2H, H6); 8.97 (s, 1H, H8); 7.69 (s, 1H, H9); 7.61 (d, 2H, J = 8.5, H11, H15); 6.94 (d, 2H, J = 8.5, H12, H14); 3.85 (m, 3H, H16). 13C NMR [Bruker XL-500, 125 MHz, d 6-CDCl3, δ (ppm)]: 122.8 (C2), 134.4 (C3), 129.3 (C4), 125.4 (C5), 34.3 (C6), 172.9 (C7), 143.6 (C9), 126.4 (C10), 128.8 (C11, C15), 114.3 (C12, C14), 161.3 (C13), 55.4 (C16). Calculation for C14H14N2O2S: M [+H] = 274.9 au.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms were placed in idealized positions and refined in riding mode, with U iso(H) values assigned as 1.2U eq of the parent atoms (1.5 times for methyl groups), with C—H distances of 0.93 (aromatic), 0.96 (CH3) and 0.97 Å (CH2), N—H distances of 0.86 Å and O—H distances of 0.82 Å (rotating OH). In (3a), the thiophene ring is disordered over two positions [population parameters 0.762 (3) and 0.238 (3)] and was refined with restraints for the bond lengths and angles in the ring. The anisotropic temperature factors for atoms S1, C2, C4 and C5 in both orientations were constrained to be equal. In the final cycles of refinement, four and two outliers were omitted for (3a) and (3b), respectively.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (3a) | (3b) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C13H12N2O2S | C14H14N2O2S |
| M r | 260.31 | 274.33 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P b c a | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 293 | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 13.0820 (8), 8.0287 (4), 24.0442 (12) | 6.5185 (2), 9.7447 (5), 10.9291 (6) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 78.327 (4), 83.070 (4), 87.013 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 2525.4 (2) | 674.63 (6) |
| Z | 8 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.25 | 0.24 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.2 × 0.05 | 0.5 × 0.15 × 0.05 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Single source at offset/far, Eos | Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Single source at offset/far, Eos |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2018 ▸) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2018 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.453, 1.000 | 0.687, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 13596, 2571, 1759 | 13795, 2752, 2238 |
| R int | 0.039 | 0.027 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.625 | 0.625 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.046, 0.109, 1.07 | 0.051, 0.145, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 2571 | 2752 |
| No. of parameters | 178 | 173 |
| No. of restraints | 80 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.18 | 0.33, −0.38 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 3a, 3b. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz5260sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3a. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603asup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3b. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603bsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603asup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603bsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
LVM thanks the Hercules Foundation for supporting the purchase of the diffractometer through project AKUL/09/ 0035.
supplementary crystallographic information
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Crystal data
| C13H12N2O2S | Dx = 1.369 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 260.31 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cell parameters from 3446 reflections |
| a = 13.0820 (8) Å | θ = 3.1–23.7° |
| b = 8.0287 (4) Å | µ = 0.25 mm−1 |
| c = 24.0442 (12) Å | T = 293 K |
| V = 2525.4 (2) Å3 | Plate, white |
| Z = 8 | 0.35 × 0.2 × 0.05 mm |
| F(000) = 1088 |
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Data collection
| Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Single source at offset/far, Eos diffractometer | 2571 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed X-ray tube, SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 1759 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.039 |
| Detector resolution: 15.9631 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω scans | h = −16→15 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2018) | k = −9→10 |
| Tmin = 0.453, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −28→30 |
| 13596 measured reflections |
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0334P)2 + 0.6755P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.07 | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 2571 reflections | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 178 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL (Sheldrick, 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 80 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0022 (6) |
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| S1A | 0.67164 (8) | 0.8283 (2) | 0.43607 (8) | 0.0718 (4) | 0.762 (3) |
| S1B | 0.6152 (4) | 0.9867 (10) | 0.3990 (3) | 0.0718 (4) | 0.238 (3) |
| C2A | 0.5667 (3) | 0.7484 (7) | 0.4673 (3) | 0.0542 (12) | 0.762 (3) |
| H2A | 0.568185 | 0.659897 | 0.492216 | 0.065* | 0.762 (3) |
| C2B | 0.4941 (11) | 0.970 (3) | 0.4213 (16) | 0.0542 (12) | 0.238 (3) |
| H2B | 0.443026 | 1.047111 | 0.413833 | 0.065* | 0.238 (3) |
| C3 | 0.47998 (16) | 0.8287 (2) | 0.45167 (8) | 0.0449 (5) | |
| C4A | 0.5018 (5) | 0.9582 (10) | 0.4141 (5) | 0.062 (2) | 0.762 (3) |
| H4A | 0.451169 | 1.026238 | 0.399205 | 0.074* | 0.762 (3) |
| C4B | 0.5719 (9) | 0.741 (3) | 0.4587 (11) | 0.062 (2) | 0.238 (3) |
| H4B | 0.575924 | 0.640913 | 0.478166 | 0.074* | 0.238 (3) |
| C5A | 0.6056 (6) | 0.9770 (11) | 0.4008 (4) | 0.100 (3) | 0.762 (3) |
| H5A | 0.633233 | 1.056338 | 0.376954 | 0.120* | 0.762 (3) |
| C5B | 0.6580 (10) | 0.818 (2) | 0.4337 (11) | 0.100 (3) | 0.238 (3) |
| H5B | 0.725438 | 0.781636 | 0.435909 | 0.120* | 0.238 (3) |
| C6 | 0.37396 (16) | 0.7786 (3) | 0.47035 (8) | 0.0506 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.377254 | 0.726825 | 0.506761 | 0.061* | |
| H6B | 0.330528 | 0.876200 | 0.472922 | 0.061* | |
| C7 | 0.33041 (15) | 0.6577 (3) | 0.42864 (8) | 0.0419 (5) | |
| O8 | 0.36037 (11) | 0.51138 (17) | 0.42613 (5) | 0.0476 (4) | |
| N9 | 0.26256 (13) | 0.7198 (2) | 0.39247 (6) | 0.0455 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.236595 | 0.816955 | 0.397669 | 0.055* | |
| N10 | 0.23452 (13) | 0.6255 (2) | 0.34641 (6) | 0.0441 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.16622 (15) | 0.6908 (2) | 0.31536 (8) | 0.0444 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.135667 | 0.790093 | 0.326364 | 0.053* | |
| C12 | 0.13478 (16) | 0.6139 (2) | 0.26302 (8) | 0.0428 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.04946 (18) | 0.6712 (3) | 0.23499 (9) | 0.0553 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.012178 | 0.759047 | 0.249952 | 0.066* | |
| C14 | 0.01803 (18) | 0.6010 (3) | 0.18517 (9) | 0.0561 (6) | |
| H14 | −0.040209 | 0.640454 | 0.167331 | 0.067* | |
| C15 | 0.07373 (17) | 0.4720 (2) | 0.16220 (8) | 0.0462 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.16018 (17) | 0.4149 (3) | 0.18911 (9) | 0.0562 (6) | |
| H16 | 0.198233 | 0.328679 | 0.173641 | 0.067* | |
| C17 | 0.19021 (17) | 0.4850 (3) | 0.23870 (9) | 0.0538 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.248657 | 0.445441 | 0.256329 | 0.065* | |
| O18 | 0.04708 (13) | 0.39577 (19) | 0.11361 (6) | 0.0620 (5) | |
| H18 | −0.003809 | 0.441085 | 0.100663 | 0.093* |
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1A | 0.0493 (6) | 0.0807 (8) | 0.0853 (7) | 0.0003 (5) | −0.0078 (5) | −0.0050 (6) |
| S1B | 0.0493 (6) | 0.0807 (8) | 0.0853 (7) | 0.0003 (5) | −0.0078 (5) | −0.0050 (6) |
| C2A | 0.065 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.047 (3) | 0.0092 (16) | −0.0120 (16) | 0.0016 (17) |
| C2B | 0.065 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.047 (3) | 0.0092 (16) | −0.0120 (16) | 0.0016 (17) |
| C3 | 0.0513 (14) | 0.0403 (11) | 0.0430 (11) | −0.0013 (10) | −0.0106 (10) | −0.0057 (9) |
| C4A | 0.060 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.072 (6) | −0.0011 (18) | −0.008 (2) | 0.015 (3) |
| C4B | 0.060 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.072 (6) | −0.0011 (18) | −0.008 (2) | 0.015 (3) |
| C5A | 0.132 (6) | 0.063 (3) | 0.103 (4) | −0.025 (3) | −0.011 (3) | 0.021 (2) |
| C5B | 0.132 (6) | 0.063 (3) | 0.103 (4) | −0.025 (3) | −0.011 (3) | 0.021 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0551 (15) | 0.0539 (13) | 0.0427 (11) | 0.0014 (11) | −0.0020 (10) | −0.0088 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0408 (13) | 0.0444 (12) | 0.0405 (11) | −0.0017 (9) | 0.0056 (9) | −0.0002 (9) |
| O8 | 0.0533 (10) | 0.0400 (8) | 0.0495 (8) | 0.0012 (7) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0005 (6) |
| N9 | 0.0489 (11) | 0.0370 (9) | 0.0506 (10) | 0.0033 (8) | −0.0043 (8) | −0.0084 (8) |
| N10 | 0.0471 (11) | 0.0408 (10) | 0.0444 (9) | −0.0029 (8) | −0.0030 (8) | −0.0029 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0451 (13) | 0.0420 (11) | 0.0461 (11) | 0.0020 (9) | 0.0006 (10) | 0.0014 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0458 (13) | 0.0404 (11) | 0.0424 (11) | −0.0007 (9) | −0.0002 (9) | 0.0024 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0611 (16) | 0.0527 (14) | 0.0520 (13) | 0.0196 (11) | −0.0082 (11) | −0.0087 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0600 (15) | 0.0569 (14) | 0.0515 (13) | 0.0146 (11) | −0.0136 (11) | −0.0038 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0553 (14) | 0.0429 (12) | 0.0405 (11) | 0.0003 (10) | −0.0008 (10) | 0.0007 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0616 (16) | 0.0536 (13) | 0.0535 (13) | 0.0137 (11) | −0.0009 (12) | −0.0088 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0516 (15) | 0.0545 (13) | 0.0553 (13) | 0.0117 (11) | −0.0082 (11) | −0.0018 (11) |
| O18 | 0.0748 (13) | 0.0574 (10) | 0.0539 (9) | 0.0122 (8) | −0.0116 (8) | −0.0129 (8) |
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1A—C2A | 1.691 (4) | C7—O8 | 1.240 (2) |
| C2A—H2A | 0.9300 | C7—N9 | 1.339 (2) |
| S1B—C2B | 1.677 (9) | N9—H9 | 0.8600 |
| C2B—H2B | 0.9300 | N9—N10 | 1.391 (2) |
| C2A—C3 | 1.357 (4) | N10—C11 | 1.277 (2) |
| C2B—C3 | 1.360 (9) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4A—H4A | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.461 (3) |
| C4B—H4B | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.382 (3) |
| S1A—C5A | 1.700 (7) | C12—C17 | 1.393 (3) |
| C4A—C5A | 1.404 (6) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5A—H5A | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.386 (3) |
| S1B—C5B | 1.688 (9) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C4B—C5B | 1.419 (9) | C14—C15 | 1.381 (3) |
| C5B—H5B | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.381 (3) |
| C3—C4A | 1.407 (4) | C15—O18 | 1.364 (2) |
| C3—C4B | 1.404 (9) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C6 | 1.512 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.376 (3) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | O18—H18 | 0.8200 |
| C6—C7 | 1.508 (3) | ||
| C4A—C5A—S1A | 107.6 (5) | C3—C4B—C5B | 114.2 (9) |
| C4B—C5B—S1B | 107.2 (8) | O8—C7—C6 | 121.54 (19) |
| S1A—C2A—H2A | 124.0 | O8—C7—N9 | 122.07 (18) |
| S1B—C2B—H2B | 124.2 | N9—C7—C6 | 116.27 (18) |
| C5A—C4A—C3 | 115.0 (5) | C7—N9—H9 | 120.4 |
| C5A—C4A—H4A | 122.5 | C7—N9—N10 | 119.29 (16) |
| C5B—C4B—H4B | 122.9 | N10—N9—H9 | 120.4 |
| C2A—S1A—C5A | 94.3 (3) | C11—N10—N9 | 115.25 (17) |
| S1A—C5A—H5A | 126.2 | N10—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| C4A—C5A—H5A | 126.2 | N10—C11—C12 | 121.81 (19) |
| C2B—S1B—C5B | 95.2 (6) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| S1B—C5B—H5B | 126.4 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.45 (18) |
| C4B—C5B—H5B | 126.4 | C13—C12—C17 | 117.57 (19) |
| C2A—C3—C4A | 111.1 (3) | C17—C12—C11 | 121.95 (19) |
| C2B—C3—C4B | 111.5 (7) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.1 |
| C4A—C3—C6 | 125.0 (3) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.7 (2) |
| C2A—C3—C6 | 123.9 (3) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.1 |
| C4B—C3—C6 | 128.0 (6) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.2 |
| C2B—C3—C6 | 120.4 (5) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.6 (2) |
| C3—C6—H6A | 110.0 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.2 |
| C3—C2A—S1A | 112.1 (3) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.6 (2) |
| C3—C2B—S1B | 111.6 (7) | O18—C15—C14 | 123.0 (2) |
| C3—C6—H6B | 110.0 | O18—C15—C16 | 117.47 (19) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 108.3 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2A—H2A | 124.0 | C17—C16—C15 | 120.3 (2) |
| C3—C2B—H2B | 124.2 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C7—C6—C3 | 108.68 (16) | C12—C17—H17 | 119.4 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 110.0 | C16—C17—C12 | 121.3 (2) |
| C3—C4A—H4A | 122.5 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.4 |
| C3—C4B—H4B | 122.9 | C15—O18—H18 | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6B | 110.0 | ||
| C2A—S1A—C5A—C4A | −0.7 (11) | C6—C3—C4B—C5B | 176.8 (17) |
| C2B—S1B—C5B—C4B | 5 (3) | C6—C3—C4A—C5A | −177.0 (8) |
| C5B—S1B—C2B—C3 | −5 (3) | C6—C7—N9—N10 | 167.45 (16) |
| C5A—S1A—C2A—C3 | 0.8 (7) | C7—N9—N10—C11 | 177.10 (18) |
| S1B—C2B—C3—C4B | 3 (3) | O8—C7—N9—N10 | −8.6 (3) |
| S1A—C2A—C3—C4A | −0.7 (5) | N9—N10—C11—C12 | 174.82 (16) |
| S1A—C2A—C3—C6 | 176.5 (3) | N10—C11—C12—C13 | 169.1 (2) |
| S1B—C2B—C3—C6 | −173.1 (14) | N10—C11—C12—C17 | −12.8 (3) |
| C2B—C3—C6—C7 | 95 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 179.8 (2) |
| C2A—C3—C6—C7 | −91.1 (5) | C11—C12—C17—C16 | −179.4 (2) |
| C4A—C3—C6—C7 | 85.7 (7) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.9 (4) |
| C4B—C3—C6—C7 | −81.0 (17) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | −1.2 (3) |
| C2A—C3—C4A—C5A | 0.1 (11) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.1 (3) |
| C2B—C3—C4B—C5B | 1 (3) | C13—C14—C15—O18 | 179.4 (2) |
| C3—C4A—C5A—S1A | 0.5 (14) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.5 (3) |
| C3—C4B—C5B—S1B | −4 (3) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | 0.1 (3) |
| C3—C6—C7—O8 | 74.2 (2) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | 1.6 (3) |
| C3—C6—C7—N9 | −101.8 (2) | O18—C15—C16—C17 | −179.0 (2) |
N'-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3a) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg3 is the centroid of the C12–C17 phenyl ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N9—H9···O8i | 0.86 | 2.12 | 2.953 (2) | 162 |
| O18—H18···O8ii | 0.82 | 1.97 | 2.782 (2) | 169 |
| C2A—H2A···O8iii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.439 (7) | 155 |
| C13—H13···Cg3iv | 0.93 | 2.89 | 3.818 (3) | 176 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y+1/2, z; (ii) x−1/2, y, −z+1/2; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Crystal data
| C14H14N2O2S | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 274.33 | F(000) = 288 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.350 Mg m−3 |
| a = 6.5185 (2) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.7447 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 5534 reflections |
| c = 10.9291 (6) Å | θ = 3.1–27.2° |
| α = 78.327 (4)° | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| β = 83.070 (4)° | T = 293 K |
| γ = 87.013 (4)° | Needle, white |
| V = 674.63 (6) Å3 | 0.5 × 0.15 × 0.05 mm |
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Data collection
| Rigaku Oxford Diffraction SuperNova, Single source at offset/far, Eos diffractometer | 2752 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed X-ray tube, SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 2238 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 15.9631 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.6° |
| ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2018) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.687, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −13→13 |
| 13795 measured reflections |
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.145 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0537P)2 + 0.5294P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2752 reflections | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 173 parameters | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.68895 (12) | 0.78924 (10) | 0.16957 (9) | 0.0734 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.5595 (4) | 0.7356 (3) | 0.3147 (3) | 0.0534 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.619153 | 0.726965 | 0.389168 | 0.064* | |
| C3 | 0.3579 (4) | 0.7066 (2) | 0.3100 (2) | 0.0436 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.3123 (4) | 0.7275 (3) | 0.1841 (2) | 0.0512 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.182310 | 0.712513 | 0.163071 | 0.061* | |
| C5 | 0.4790 (4) | 0.7727 (3) | 0.0935 (2) | 0.0497 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.476097 | 0.790729 | 0.006852 | 0.060* | |
| C6 | 0.2002 (4) | 0.6708 (3) | 0.4234 (2) | 0.0479 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.265853 | 0.615910 | 0.493142 | 0.057* | |
| H6B | 0.093072 | 0.615347 | 0.404620 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 0.1056 (3) | 0.8042 (3) | 0.4589 (2) | 0.0418 (5) | |
| O8 | −0.0513 (2) | 0.86009 (19) | 0.41630 (16) | 0.0508 (4) | |
| N9 | 0.2051 (3) | 0.8658 (2) | 0.53376 (18) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.160089 | 0.945717 | 0.549350 | 0.050* | |
| N10 | 0.3778 (3) | 0.8031 (2) | 0.58594 (17) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.4621 (3) | 0.8739 (2) | 0.6517 (2) | 0.0411 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.406000 | 0.961642 | 0.660165 | 0.049* | |
| C12 | 0.6438 (3) | 0.8207 (2) | 0.7139 (2) | 0.0372 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.7354 (4) | 0.9057 (2) | 0.7794 (2) | 0.0423 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.679005 | 0.994741 | 0.782354 | 0.051* | |
| C14 | 0.9070 (4) | 0.8605 (2) | 0.8396 (2) | 0.0444 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.966061 | 0.919004 | 0.882266 | 0.053* | |
| C15 | 0.9921 (3) | 0.7276 (2) | 0.8368 (2) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.9037 (4) | 0.6415 (2) | 0.7722 (2) | 0.0442 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.960075 | 0.552276 | 0.769944 | 0.053* | |
| C17 | 0.7322 (4) | 0.6880 (2) | 0.7113 (2) | 0.0435 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.674636 | 0.629647 | 0.667808 | 0.052* | |
| O18 | 1.1602 (3) | 0.69079 (19) | 0.90073 (17) | 0.0565 (5) | |
| C19 | 1.2603 (4) | 0.5592 (3) | 0.8926 (3) | 0.0634 (8) | |
| H19A | 1.307244 | 0.557208 | 0.806228 | 0.095* | |
| H19B | 1.164788 | 0.485433 | 0.925510 | 0.095* | |
| H19C | 1.376398 | 0.546115 | 0.940466 | 0.095* |
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0554 (5) | 0.0848 (6) | 0.0861 (6) | −0.0076 (4) | 0.0084 (4) | −0.0394 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0441 (13) | 0.0592 (16) | 0.0640 (16) | 0.0019 (11) | −0.0103 (12) | −0.0270 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0445 (13) | 0.0376 (12) | 0.0529 (14) | −0.0006 (9) | −0.0085 (10) | −0.0175 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0541 (15) | 0.0493 (14) | 0.0568 (15) | −0.0023 (11) | −0.0156 (12) | −0.0207 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0528 (14) | 0.0505 (14) | 0.0506 (14) | −0.0044 (11) | 0.0003 (11) | −0.0238 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0503 (14) | 0.0436 (13) | 0.0526 (14) | −0.0098 (10) | −0.0110 (11) | −0.0108 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0368 (12) | 0.0511 (13) | 0.0368 (11) | −0.0088 (10) | −0.0037 (9) | −0.0056 (10) |
| O8 | 0.0366 (9) | 0.0680 (12) | 0.0511 (10) | −0.0008 (8) | −0.0129 (7) | −0.0152 (8) |
| N9 | 0.0364 (10) | 0.0489 (11) | 0.0424 (10) | 0.0032 (8) | −0.0114 (8) | −0.0121 (8) |
| N10 | 0.0381 (10) | 0.0472 (11) | 0.0386 (10) | 0.0011 (8) | −0.0096 (8) | −0.0069 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0422 (12) | 0.0396 (12) | 0.0021 (9) | −0.0073 (9) | −0.0087 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0370 (11) | 0.0399 (12) | 0.0343 (11) | −0.0020 (9) | −0.0055 (9) | −0.0052 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0485 (13) | 0.0361 (12) | 0.0436 (12) | 0.0034 (10) | −0.0101 (10) | −0.0098 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0498 (13) | 0.0439 (13) | 0.0444 (13) | −0.0029 (10) | −0.0149 (10) | −0.0143 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0393 (12) | 0.0467 (13) | 0.0356 (11) | −0.0006 (10) | −0.0088 (9) | −0.0034 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0482 (13) | 0.0365 (12) | 0.0491 (13) | 0.0036 (10) | −0.0117 (11) | −0.0094 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0470 (13) | 0.0408 (12) | 0.0465 (13) | −0.0032 (10) | −0.0113 (10) | −0.0135 (10) |
| O18 | 0.0538 (10) | 0.0595 (11) | 0.0613 (11) | 0.0109 (8) | −0.0284 (9) | −0.0142 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0560 (16) | 0.0645 (18) | 0.0690 (18) | 0.0175 (13) | −0.0214 (14) | −0.0085 (14) |
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C2 | 1.700 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| S1—C5 | 1.715 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.456 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.396 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.368 (3) | C12—C17 | 1.393 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.415 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C6 | 1.507 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.374 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.403 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.387 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.387 (3) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C15—O18 | 1.363 (3) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.511 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.379 (3) |
| C7—O8 | 1.230 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N9 | 1.348 (3) | O18—C19 | 1.422 (3) |
| N9—H9 | 0.8600 | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| N9—N10 | 1.382 (2) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| N10—C11 | 1.277 (3) | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C2—S1—C5 | 93.48 (13) | N10—C11—C12 | 121.7 (2) |
| S1—C2—H2 | 123.7 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.2 |
| C3—C2—S1 | 112.5 (2) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.1 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 123.7 | C17—C12—C11 | 123.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 111.0 (2) | C17—C12—C13 | 117.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C6 | 124.5 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.3 |
| C4—C3—C6 | 124.3 (2) | C14—C13—C12 | 121.4 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 122.7 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 114.5 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 122.7 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.0 (2) |
| S1—C5—H5 | 125.7 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—S1 | 108.50 (19) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 125.7 | O18—C15—C14 | 116.0 (2) |
| C3—C6—H6A | 109.8 | O18—C15—C16 | 124.5 (2) |
| C3—C6—H6B | 109.8 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C3—C6—C7 | 109.57 (19) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.1 (2) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 108.2 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 109.8 | C12—C17—H17 | 119.4 |
| C7—C6—H6B | 109.8 | C16—C17—C12 | 121.2 (2) |
| O8—C7—C6 | 121.7 (2) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.4 |
| O8—C7—N9 | 120.2 (2) | C15—O18—C19 | 117.5 (2) |
| N9—C7—C6 | 117.9 (2) | O18—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C7—N9—H9 | 119.3 | O18—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C7—N9—N10 | 121.3 (2) | O18—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| N10—N9—H9 | 119.3 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C11—N10—N9 | 115.4 (2) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| N10—C11—H11 | 119.2 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| S1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (3) | N10—C11—C12—C13 | 176.9 (2) |
| S1—C2—C3—C6 | −173.66 (19) | N10—C11—C12—C17 | −3.1 (4) |
| C2—S1—C5—C4 | 0.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 180.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.2 (3) | C11—C12—C17—C16 | −179.6 (2) |
| C2—C3—C6—C7 | 84.9 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.4 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—S1 | −0.5 (3) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | 0.4 (3) |
| C3—C6—C7—O8 | 90.8 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.4 (4) |
| C3—C6—C7—N9 | −85.4 (3) | C13—C14—C15—O18 | −179.0 (2) |
| C4—C3—C6—C7 | −88.8 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.0 (4) |
| C5—S1—C2—C3 | −1.0 (2) | C14—C15—O18—C19 | −175.7 (2) |
| C6—C3—C4—C5 | 174.3 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | −0.4 (4) |
| C6—C7—N9—N10 | −5.8 (3) | C16—C15—O18—C19 | 4.9 (4) |
| C7—N9—N10—C11 | 177.8 (2) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | 0.0 (3) |
| O8—C7—N9—N10 | 177.97 (19) | O18—C15—C16—C17 | 179.4 (2) |
| N9—N10—C11—C12 | 179.26 (19) |
N'-[1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)benzylidene]-2-(thiophen-3-yl)acetohydrazide (3b) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the S1/C1–C5 thiophene ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N9—H9···O8i | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.935 (3) | 179 |
| C6—H6A···N10 | 0.97 | 2.44 | 2.782 (3) | 100 |
| C13—H13···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.68 | 3.611 (2) | 179 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1.
References
- Bharti, S. K., Nath, G., Tilak, R. & Singh, S. K. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 651–660. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- El-Sayed, H. A., Moustafa, A. H., El-Moneim, M. A., Awad, H. M. & Esmat, A. (2018). J. Pharm. Appl. Chem. 4, 125–131.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Loncle, C., Brunel, J. M., Vidal, N., Dherbomez, M. & Letourneux, Y. (2004). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 39, 1067–1071. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 3814–3816. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N. L., Tran, T. D., Nguyen, T. C., Duong, K. L., Pfleger, J. & Vu, Q. T. (2016). Vietnam. J. Chem. 54, 259–263.
- Papakonstantinou-Garoufalias, S., Pouli, N., Marakos, P. & Chytyroglou-Ladas, A. (2002). Farmaco, 57, 973–977. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2018). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, M. A. & Jayatilaka, D. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 19–32.
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer 17. University of Western Australia. http://hirshfeldsurface.net
- Vu, Q. T., Nguyen, N. L., Duong, K. L. & Pfleger, J. (2016). Vietnam. J. Chem. 54, 730–735.
- Vu Quoc, T., Nguyen Ngoc, L., Nguyen Tien, C., Thang Pham, C. & Van Meervelt, L. (2017). Acta Cryst. E73, 901–904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wardakhan, W. W., Eid, E.-S. N. N & Mohareb, R. M. (2013). Acta Pharm. 63, 45–57. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M., Sinha, R. R., Kumar, S., Bahadur, I. & Ebenso, E. E. (2015). J. Mol. Liq. 208, 322–332.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 3a, 3b. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz5260sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3a. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603asup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3b. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603bsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603asup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019008892/rz52603bsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report











